Fiber Connector Types play a pivotal role in ensuring efficient and reliable communication in modern networks. Among the many types available, LC, SC, FC, ST, MTP, and MPO connectors each offer unique features tailored for specific applications. Understanding the differences between these connectors is crucial for selecting the right one for your networking needs. In this article, we’ll explore the characteristics, use cases, and advantages of each type, providing you with a comprehensive guide to fiber optic connector selection.
What is a Fiber Connector?
A fiber connector is a detachable passive optical component used to connect fiber to fiber, a light source to fiber, and fiber to a detector, ensuring optimal light coupling into the receiving fiber. While there are hundreds of different fiber connector types on the market, only about a dozen are widely used and can be categorized into single-fiber, duplex fiber connectors (such as FC, LC, SC), and multi-fiber connectors (such as MTP/MPO).
Fiber connectors are integral to the reliability and performance of optical transmission systems. A high-quality connector minimizes light loss due to reflection or misalignment of the fibers.
A superior fiber connector can be assessed based on the following criteria:
- Low loss.
- Small size and lightweight design.
- Ease of installation and operation.
- Cost-effectiveness.
- High reliability.
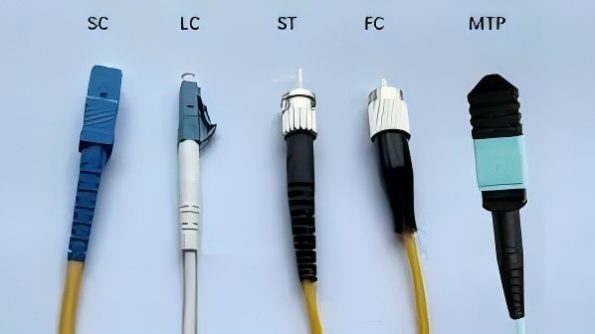
In today’s data center applications, smaller, simpler, and multi-fiber fiber connectors have gradually replaced larger and more complex types, achieving a higher density of fiber ports per unit of rack space. This article will introduce the widely used fiber connector types, including FC, SC, LC, ST, and MTP/MPO connectors.
Fiber Connector Types – SC
The SC fiber connector, short for square fiber optical connector, features a square push-pull structure with a ferrule diameter of 2.5mm. A spring inside the flange ensures a secure connection, indicated by a distinctive click. SC connectors are commonly used in Gigabit Ethernet networks, datacom, and telecom applications. They offer advantages such as low cost, easy push-pull operation, low insertion loss, and good compression strength, making them widely used since the 1990s.
Fiber Connector Types – FC
FC (Ferrule Connector) features a round screw structure and is slightly more complex to install than the push-pull SC fiber connector. Careful alignment is required, and there is a risk of scratching the fiber end face during insertion. The ferrule diameter of the FC is also 2.5mm. FC connectors are generally used in datacom, telecom, measurement equipment, and single-mode lasers. However, they have been gradually replaced by SC and LC connectors, which offer equivalent performance but with faster connection speeds.
Fiber Connector Types – LC
The LC fiber connector, adopting a modular jack latch structure, offers significant ease of operation. With a ferrule diameter of only 1.25mm, it is half the size of SC and FC connectors, contributing to increased density of fiber connectors in optical fiber wiring frames. The LC connector has dominated the market, being widely used in both single-mode and multimode SFF (Small Form Factor) transceivers and gradually replacing SC due to its smaller size.
Fiber Connector Types – ST
The ST optical connector features a bayonet structure, requiring careful alignment of the index tab with a slot during insertion. The spring-loaded structure makes the ST fiber optical connector require significant effort to push and twist. The ferrule diameter is also 2.5mm. ST connectors are typically used in multimode datacom but have also been replaced by SC or LC connectors.
Fiber Connector Types – MTP/MPO
The evolution of fiber connectors can be divided into two stages. The first stage involves the transition from FC, ST, SC connectors to LC, aiming for space-saving and miniaturization. The second stage is the evolution from LC to MTP/MPO, which not only achieves space-saving but also meets the requirements of multi-fiber applications. MTP/MPO connectors are available in capacities ranging from 2-fiber to 72-fiber.
MTP connectors are used interchangeably with MPO and are typically applied in high-speed data center and LAN applications.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fiber Connectors
1.What is the difference between LC and SC fiber optic connectors?
LC vs SC Size – LC is smaller than SC, with a diameter of 1.25mm compared to 2.5mm for SC, making LC more suitable for high-density applications. Its compact size allows for twice the port density on a faceplate compared to SC connectors.
LC vs SC Connection Handling – LC connectors feature a latch structure with a locking tab for secure cable retention, while SC connectors use a push-pull structure with a latch for secure cable retention.
2.How to terminate SC with LC connector?
SC to LC adapter assemblies can facilitate the connection between an SC connector and an LC connector. Additionally, SC-LC fiber cables, which terminate with an SC interface at one end and an LC interface at the other, are also useful for such connections.