As an indispensable transmission device in modern networks, optical modules undertake the key task of high-speed data transmission. Whether in data centers, cloud computing platforms, or in the telecommunications industry, the role of optical modules is crucial. With the continuous growth of network demand, optical modules with different rates have been launched one after another, among which 100G, 400G and 800G optical modules have become the focus of attention. So, what exactly is an optical module? What are the differences in speed, application scenarios and technical characteristics? Next, we will analyze these issues in detail to help you better understand the core functions of optical modules and their development trends.
1.What Is An Optical Module?
An optical module is a device that converts electrical signals into optical signals and transmits them through optical fibers. Its core function is to convert electrical signals into optical signals at the transmitting end and convert optical signals back to electrical signals at the receiving end.
2.Differences And Characteristics Of 100G, 400G, And 800G Optical Modules
The rates of optical modules are different, such as 100G, 400G, and 800G. These numbers represent the data transmission rate of the optical module in Gbps (gigabits per second).
a.100G optical module
100G optical module refers to an optical module with a transmission rate of 100Gbps (gigabits per second). This module is usually packaged in QSFP28 (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Double Density), which contains four independent 25Gbps optical signal transmission channels. 100G optical modules are widely used in data centers, high-speed network connections, and various application scenarios that require high-speed data transmission.

b.400G optical module
With the growth of data transmission demand, 400G optical modules have emerged with a transmission rate of 400Gbps. 400G optical modules not only improve data throughput, but also improve the bandwidth and port density of data centers through optimized design. This module supports a variety of transmission distances and fiber types, which can meet the needs of different network architectures. 400G optical modules are key components for building future high-speed, high-capacity network systems.
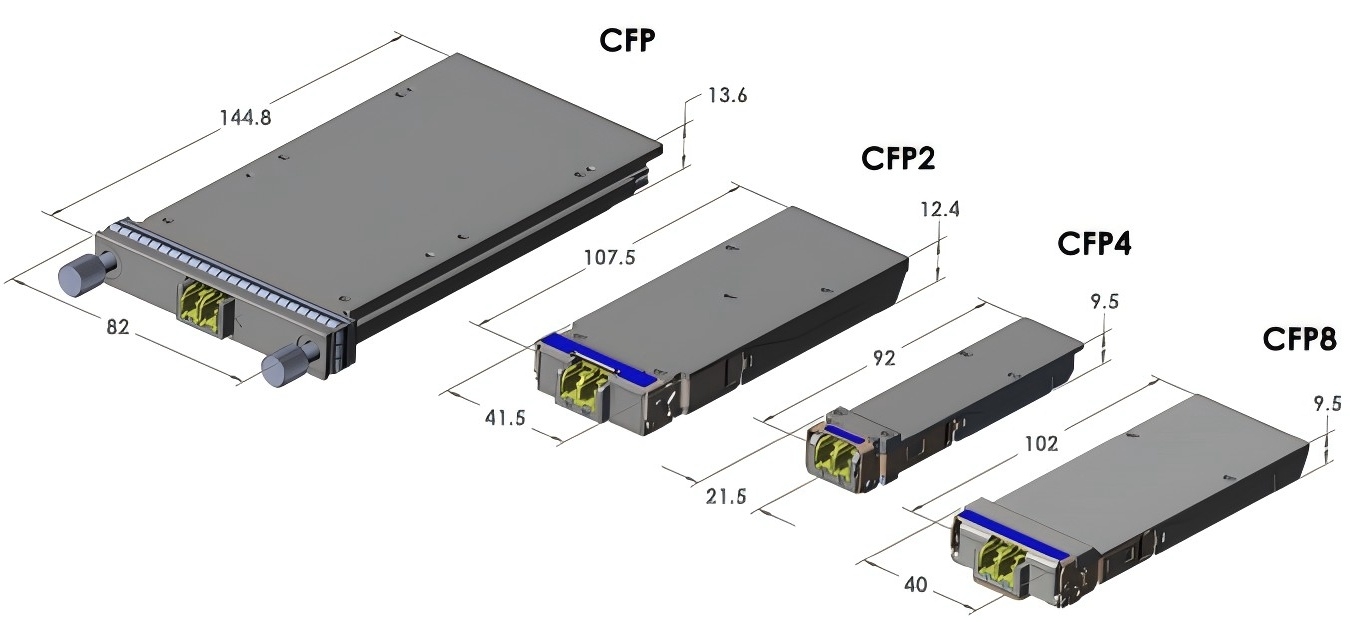
c.800G optical module
800G optical modules represent the latest development of optical module technology, with a transmission rate of 800Gbps. This module is designed with technological advancement in mind to achieve competitive single-mode fiber solutions. 800G optical modules are developed to meet the growing demand for network bandwidth, especially in data centers and large-scale network infrastructure. With the advancement of technology, 800G optical modules are expected to become a key technology to support higher data rates and larger data capacities.

The evolution of optical module rates from 100G to 400G and then to 400G reflects the continuous pursuit of higher speeds and larger capacities in the field of data communications. Here are the differences between them:
a.100G optical module: This optical module has a data transmission rate of 100Gbps. It usually adopts QSFP28 packaging and contains 4 independent optical signal transmission channels, each with a rate of 25Gbps. 100G optical module is the basic equipment for high-speed data transmission and is widely used in data centers and high-speed network connections.
b.400G optical module: With the development of network technology, 400G optical module came into being, and its transmission rate reached 400Gbps. This optical module not only improves data throughput, but also optimizes the bandwidth and port density of the data center. The 400G optical module is designed to support network requirements of different rates from 100M to 1T and is a key component for building high-speed network systems.
c.800G optical module: The 800G optical module represents the latest progress in optical module technology, with a transmission rate of 800Gbps. This optical module defines two schemes in the 800G pluggable MSA (Multi-Source Agreement): 800G-SR8 and 800G-FR4. The 800G-SR8 scheme takes into account technological advancement to achieve a competitive single-mode fiber solution, while the 800G-FR4 scheme focuses on the integration of new FEC (forward error correction) technology to ensure interoperability. The development of 800G optical modules heralds the high density and cost-effectiveness of future network technology.
Conclusion:
Through an in-depth comparison of 100G, 400G and 800G optical modules, we can clearly see their significant differences in transmission rate, performance and applicable scenarios. With the continuous advancement of technology, the speed of optical modules is gradually increasing to meet the growing data demand. Whether it is upgrading the existing network or planning the future network infrastructure, choosing the right optical module is particularly important. We hope that through the relevant analysis provided by Fiber-Life, you can better understand the logic behind these technologies and make more informed choices.