In today’s digital world, reliable and high-speed internet access is essential for communication, business operations, and economic growth. Internet bandwidth can be delivered to homes and offices through two primary wired methods: Ethernet cables, which transmit data via electrical pulses over copper wires, and fiber optic cables, which use light for data transmission.
This guide explores the key differences between Ethernet and fiber optic cables, their speeds, advantages, and which option is best suited for different applications.

What is Ethernet?
Ethernet has been a standard in networking for decades. It was originally developed by Xerox in the 1970s and was commercially introduced in 1980. Ethernet transmits data using electrical signals over copper wires, which is inherently slower than fiber optics. However, it has significantly evolved over time to offer higher speeds.

Ethernet Speed Evolution
Initially, Ethernet networks were limited to 10 Mbps (Megabits per second). Today, advancements have led to much faster speeds:
- Fast Ethernet: 100 Mbps
- Gigabit Ethernet: 1,000 Mbps (1 Gbps)
- Cat6 Ethernet: Supports up to 10 Gbps
How Ethernet Works
Ethernet cables transmit data via electrical pulses. Most Ethernet cables, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7, consist of four twisted pairs of 24-gauge copper wires. Each wire transmits binary data in the form of electrical voltage changes, where:
- “1” represents a voltage pulse
- “0” represents no voltage pulse
Limitations of Ethernet
Despite improvements, Ethernet has certain drawbacks:
- Susceptibility to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) – Electrical signals can be disrupted by nearby devices.
- Security Risks – Since data is transmitted electrically, it can be intercepted and manipulated through hardware-based attacks.
- Distance Limitations – Copper-based transmission experiences signal degradation beyond 100 meters.
What is Fiber Optic Technology?
Fiber optics offer a more advanced method of data transmission by using light instead of electricity. While its widespread use in homes and offices is relatively recent, fiber optic technology has been around for over a century. In fact, NASA’s Apollo 11 mission in 1969 used fiber optics for television camera transmissions.

How Fiber Optic Cables Work
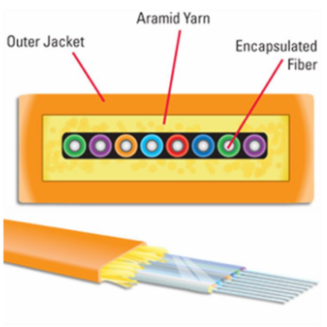
Fiber optic cables are made of thin strands of pure glass (fiber core) that carry data in the form of light pulses. There are two primary types of fiber optic cables:
- Single-Mode Fiber (SMF) – Uses laser light for transmission and is ideal for long-distance applications.
- Multimode Fiber (MMF) – Uses LED light, allowing multiple light paths for shorter distances.
Data is transmitted as binary signals:
- Light “on” (1)
- Light “off” (0)
Fiber Optic Speed & Performance
Fiber optic cables support significantly higher speeds than Ethernet. Standard transmission rates range from 10 Mbps to 10 Gbps, but some advanced fiber cables can achieve speeds of up to 100 Tbps (Terabits per second).
Advantages of Fiber Optics
- Higher Speeds – Can support data rates beyond 100 Gbps.
- Longer Distances – Can transmit signals over miles without signal loss, unlike Ethernet.
- Greater Security – Unlike copper wires, fiber does not emit electromagnetic signals, making it nearly impossible to tap into.
- Less Interference – Immune to EMI, ensuring more stable connections.
Ethernet vs. Fiber Optic: A Detailed Comparison
| Feature | Ethernet (Copper-Based) | Fiber Optic |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 10 Gbps (Cat6) | 10 Gbps to 100 Tbps |
| Signal Medium | Electrical pulses over copper | Light pulses over glass fibers |
| Interference Resistance | Prone to EMI | Immune to EMI |
| Maximum Distance | 100m (without a booster) | Over 100km (with amplifiers) |
| Security | Susceptible to hacking | Highly secure, difficult to tap |
| Installation Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment |
| Common Usage | Home networks, offices, small businesses | Data centers, ISPs, high-speed networks |
Which One Should You Choose?
When to Use Ethernet
- For cost-effective solutions – Ethernet is more affordable for small businesses and home networks.
- For simple installations – Ethernet requires minimal setup compared to fiber.
- For short-distance connectivity – Suitable for internal office networking and home setups.
When to Use Fiber Optics
- For long-distance data transmission – Fiber excels in large campuses, data centers, and ISPs.
- For high-speed and bandwidth-intensive applications – Best for cloud computing, video streaming, and large-scale enterprise networks.
- For maximum security and reliability – Less prone to external hacking and interference.
Conclusion
Both Ethernet and fiber optic cables play essential roles in networking. While Ethernet remains the primary choice for most consumer and business applications, fiber optics is the future of high-speed internet infrastructure. As global data demands increase, fiber technology is set to become the dominant method of internet delivery.
Many businesses and communities are investing in fiber optic networks to attract companies that require high bandwidth and reliable connectivity. The continued expansion of fiber infrastructure ensures that more homes and offices will soon benefit from faster, more secure, and more efficient internet connectivity.
Upgrade Your Network with Fiber-Life
Fiber-Life provides high-quality Ethernet and fiber optic solutions tailored to your networking needs. Whether you need Cat6 Ethernet cables for office connectivity or fiber optic solutions for high-speed data transfer, we offer a full range of products to optimize your network.
Why Choose Fiber-Life?
- Premium-Quality Cables – Designed for superior performance and durability.
- Wide Selection – From standard Ethernet to advanced fiber optic solutions.
- Expert Support – Our team helps you select the right cables for your setup.
Explore Fiber-Life’s range of networking solutions today and take your internet connectivity to the next level!