Navigating the intricate realm of fiber optics may initially seem daunting, but fear not—our expertise is here to guide you. Whether you’re setting up a high-speed network at home, upgrading your office connectivity, or planning a complex installation for your business, choosing the right type of fiber optic cable is crucial. The choice you make can significantly impact your network’s performance, reliability, and future scalability.
At FiberLife, we are committed to assisting you with these decisions with ease and confidence. Our mission is to continuously provide value to our global clientele in the fiber optic communications sector through top-tier products and unparalleled service. We understand the array of options can be perplexing, but we are here to demystify the process. Today, we will elucidate the key distinctions between Simplex and Duplex Fiber Optic Cables, exploring their unique attributes, benefits, and ideal applications. Our aim is to arm you with the knowledge necessary to make an informed decision tailored to your precise needs.
1. Basic Definitions
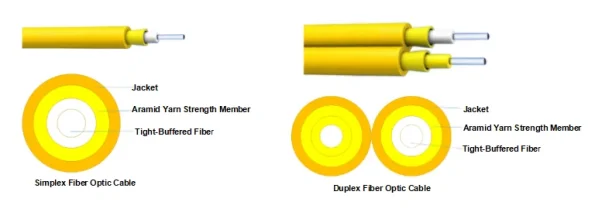
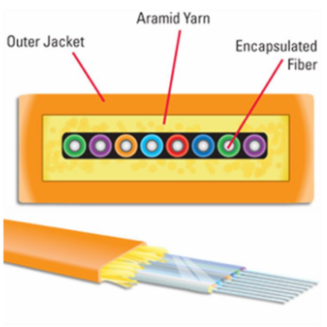
Simplex Fiber Optic Cables:
Simplex cables are characterized by their singular fiber, facilitating unidirectional data transmission. They are well-suited for scenarios where one-way communication is requisite, such as in TV broadcasting and sensor data transmission. Their construction is streamlined, typically consisting of a central core, a reflective cladding, and a robust protective outer layer.
Duplex Fiber Optic Cables:
Duplex cables feature two fibers, enabling bidirectional communication. They are available in half-duplex (allowing data transmission in both directions but not simultaneously) and full-duplex (enabling simultaneous send and receive) configurations. Commonly utilized in network communications and telephone lines, duplex cables are designed for applications necessitating two-way data interchange. The parallel arrangement of fibers in duplex cables makes them slightly bulkier than simplex cables but significantly enhances their functionality.
2. Working Principles
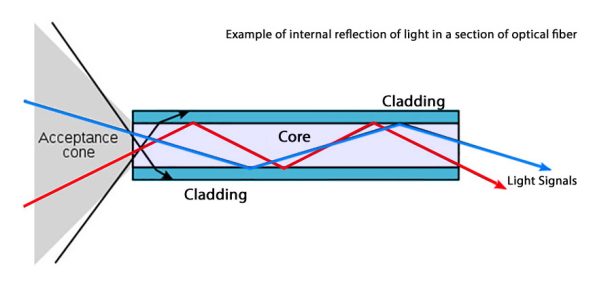
Simplex Fiber Optic Cables:
These cables operate on a principle of unidirectional data flow from sender to receiver. This is highly efficient for applications such as security camera systems, where data from the camera only needs to be transmitted to a recording device. The singular fiber negates the need for complex switching or routing mechanisms, thereby streamlining system design and economizing on costs.
Duplex Fiber Optic Cables:
Duplex cables support two-way communication. In full-duplex mode, each fiber is dedicated to a single direction of data transmission, allowing for the simultaneous sending and receiving of data. This is essential for applications like internet connections and telecommunications, where continuous two-way data flow is imperative. For instance, in a full-duplex system, one fiber can manage the upload stream, while the other manages the download stream, significantly enhancing efficiency and reducing latency.
3. Technical Parameter Comparison
Bandwidth and Speed:
Duplex Fiber Optic Cables generally provide a more capacious bandwidth and swifter data transmission rates than simplex cables, owing to their capacity for bidirectional traffic management. In high-speed internet applications, duplex cables can offer faster simultaneous upload and download speeds, crucial for environments requiring rapid and reliable data transfer, such as corporate networks or data centers.
Transmission Distance:
Both simplex and duplex cables can support long-distance transmission, yet duplex cables often excel in maintaining signal integrity over greater distances. This makes them preferable for extensive network infrastructures, such as those in large corporate settings. The ability to transmit data over long distances without significant signal degradation is a key advantage of fiber optic technology, with duplex cables standing out due to their enhanced bandwidth and minimized signal interference.
Reliability and Stability:
Duplex cables tend to offer higher reliability and stability, especially in environments demanding robust network performance. Their capacity for two-way communication diminishes the risk of data bottlenecks, making them apt for critical applications like data centers. Additionally, the use of two fibers can provide redundancy, ensuring that if one fiber fails, the other can continue to operate, thereby sustaining network uptime.
4. Application Scenarios
Simplex Fiber Optic Cables in Security Systems:
Facilitating the reliable transmission of video feeds from surveillance cameras to monitoring stations, simplex cables excel in scenarios requiring unidirectional data flow.
Sensor Data:
Simplex cables can efficiently manage the one-way data flow from sensors to monitoring systems, making them ideal for environmental monitoring and industrial automation.
Duplex Fiber Optic Cables in Internet and Network Connections:
Enabling fast and reliable internet services with simultaneous upload and download capabilities, duplex cables support high-speed internet connections, providing seamless and uninterrupted data flow for both personal and business use.
Telecommunications:
Supporting voice and data transmission in phone networks, duplex cables ensure clear and uninterrupted communication, making them essential for modern telecommunication systems.
Data Centers:
Facilitating robust and efficient data exchange within and between data centers, the high bandwidth and reliability of duplex cables make them indispensable for data center operations, where large volumes of data need to be transferred quickly and securely.
5. Installation and Maintenance
Simplex Fiber Optic Cables:
The installation of simplex cables is relatively straightforward due to their single-fiber design. They require less space and are easier to route through conduits. Maintenance is further simplified, with a reduced number of components demanding management and troubleshooting. The simplicity of simplex cables makes them a cost-effective choice for many applications, particularly in environments where space is limited or where the network layout is uncomplicated.
Duplex Fiber Optic Cables:
While duplex cables offer enhanced performance, their installation can be more complex. They necessitate precise routing to ensure both fibers are correctly connected and functioning. Maintenance involves regular checks on both fibers to ensure they are transmitting data accurately. This complexity is offset by the greater functionality and reliability that duplex cables provide, making them a worthwhile investment for more demanding network environments.
6. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Purchase Cost:
Simplex Fiber Optic Cables typically come with a lower price tag, attributable to their streamlined design, making them an economical choice for applications not requiring bidirectional communication. The reduced initial cost of simplex cables makes them an attractive option for budget-conscious projects or for applications where one-way communication is sufficient.
Long-Term Investment:
Although duplex cables may have a higher initial cost, they provide better value over time for applications benefiting from their two-way communication capabilities. Their higher bandwidth and speed can result in significant performance improvements and cost savings. In environments where network performance and reliability are paramount, the long-term advantages of duplex cables can surpass the higher upfront costs.
7. Environmental Sustainability
Materials and Manufacturing Process:
Both simplex and duplex fiber optic cables are crafted to be environmentally conscious, with minimal environmental impact during manufacturing. However, duplex cables, with their superior performance, can potentially reduce the overall amount of cabling necessary, leading to less material use and waste. The utilization of sustainable materials and manufacturing processes can further amplify the environmental benefits of fiber optic cables.
Disposal and Recycling:
Fiber optic cables are generally recyclable, but proper disposal is crucial to minimize environmental impact. Custom fiber optic cables, tailored for specific applications, may offer enhanced sustainability features such as reduced materials or improved recyclability. Opting for environmentally friendly options and adhering to proper disposal guidelines can assist in reducing the ecological footprint of fiber optic installations.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the decision between Simplex and Duplex Fiber Optic Cables hinges on the unique demands and operational prerequisites of your project. Simplex cables are cost-effective and suitable for unidirectional data transmission, making them ideal for applications like sensor data and security systems. Duplex cables, conversely, offer higher performance for bidirectional communication, perfect for internet connections, telecommunications, and data centers.
For those seeking a dependable and high-performing solution for straightforward, one-way communication needs, we wholeheartedly endorse the Simplex Tight Buffer Round Indoor Fiber Optic Cable. It offers excellent value for its performance, ensuring reliable data transmission in various settings. For more demanding applications that require robust two-way communication, the OM4 Multimode Duplex Zipcord Tight Buffer Plenum Indoor Fiber Optic Cable is your best bet. Its dual-fiber design ensures fast and reliable data transmission in both directions, making it a top choice for high-speed internet and network connectivity, particularly in complex indoor environments.
To explore these products and more, visit our website at FiberLife. We offer a comprehensive range of fiber optic solutions designed to meet your specific needs. Our team of experts is always ready to assist you in making the best choice.