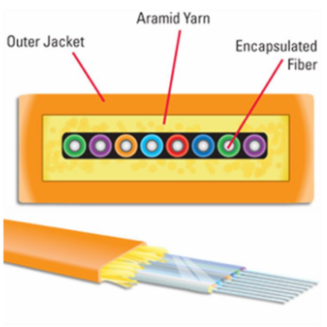
In the glorious era of optical communications, fiber optic patch cords have become an indispensable basic component for building modern optical networks with their excellent performance and diverse types. Fiber optic manufacturers have launched a series of fiber optic patch cords for different application scenarios, including but not limited to MPO/LC/SC/FC/ST, etc. They have their own characteristics and complement each other. This article will deeply analyze the classification and characteristics of these fiber optic patch cords to help you make wise choices when wiring.
Diversified classification of fiber optic patch cords

Fiber optic patch cords can be divided into MPO/MTP, LC, SC, FC, ST and other types according to the connector type. Although they share similar component structures—connectors and optical cables, their respective characteristics and performance determine their irreplaceability in specific application scenarios.
LC fiber optic patch cord: the darling of high-density wiring

LC fiber optic patch cords, with their compact connectors with a diameter of 1.25mm, have become the first choice for high-density wiring in computer rooms and data centers. With the advancement of technology, ultra-low insertion loss LC fiber patch cords and one-tube dual-core LC fiber patch cords have appeared on the market. They reduce the insertion loss to 0.12dB by adopting innovative technologies such as LL technology, providing strong support for long-distance transmission.
One-tube dual-core LC fiber patch cord: This patch cord uses a specially designed LC uniboot connector to achieve bidirectional transmission in a single optical fiber, greatly improving space utilization, saving wiring time and cost, and is especially suitable for space-constrained environments.
SC fiber patch cord: A powerful assistant for telecommunications and data networks
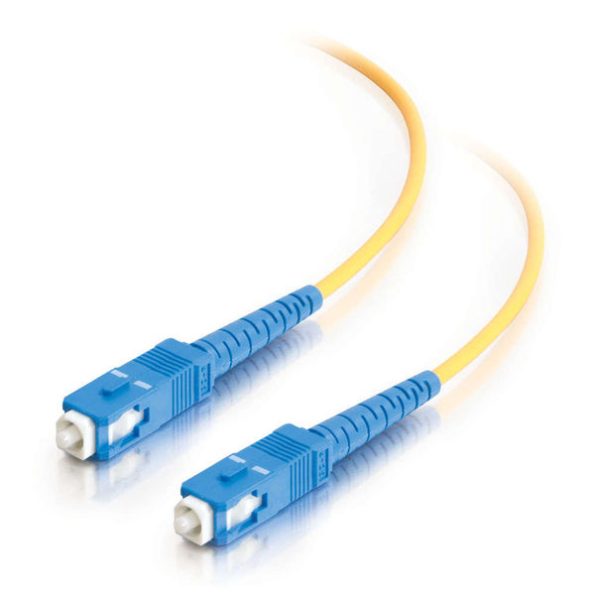

SC fiber patch cords, with their 2.5mm diameter SC connectors, are known as large square connectors. They are widely used in telecommunications and data network systems for their push-pull structure and plug-and-play features.
MPO/MTP fiber patch cords: Pioneers in high-speed data communications
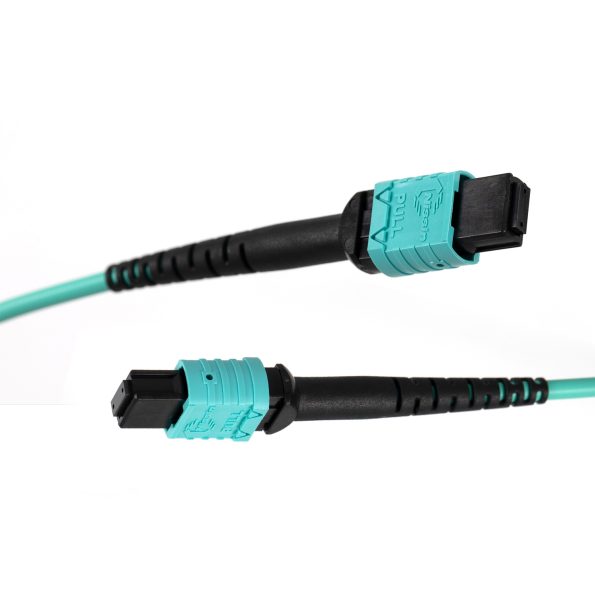

MPO/MTP fiber patch cords, with their multi-core fiber connector design, can accommodate 6 to 144 optical fibers, making them the best in high-speed data communication systems, especially suitable for 40G/100G direct connection and interconnection.
Other fiber jumpers: diversified solutions
There are also fiber jumpers such as MTRJ, MU, DIN, and E2000 on the market. They meet the needs of specific application scenarios with their unique design and performance.
Composition structure and application environment of fiber jumpers
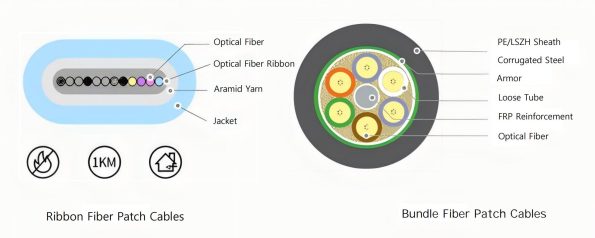
Fiber jumpers can be divided into ribbon and bundle according to their composition structure. Ribbon fiber jumpers save wiring costs and space with their flat shape and high fiber density. And bundle fiber jumpers, with their circular structure, are mainly used for indoor integrated wiring.
According to the application environment, fiber jumpers are divided into conventional and reinforced types. Conventional fiber jumpers are light and low-cost, suitable for most indoor environments. Reinforced fiber jumpers are designed for harsh outdoor environments and have waterproof and high temperature resistance.
Material and transmission mode of fiber jumpers
PVC and LSZH are common sheath materials for fiber jumpers. The former is flexible and suitable for indoor wiring; the latter is often used in public places such as subways and tunnels due to its flame retardant properties. Fiber jumpers can be divided into simplex and duplex according to the number of optical fiber cores, and can be divided into single-mode and multi-mode according to the optical transmission mode to meet the needs of different transmission distances and rates.
Polishing Types and Production Processing of Fiber Patch Cords

There are three types of polishing for fiber patch cords: PC, UPC, and APC. They each have their own advantages in insertion loss and return loss. In terms of production and processing technology, field-terminated connector fiber patch cords provide flexible configuration of optical cable length, while factory-terminated connector fiber patch cords simplify the installation process with their plug-and-play features.
Conclusion
The selection of fiber patch cords is a technical job. Faced with many types of fiber patch cords on the market, it is crucial to understand their characteristics and applicable scenarios. Whether it is the LC uniboot connector that pursues high-density wiring or the reinforced fiber patch cord that adapts to harsh environments, choosing the right fiber patch cord can maximize the performance and reliability of the network. If you have any questions about your choice, you may wish to seek guidance from professionals to ensure that your network cabling is both efficient and economical.