PLC optical splitters (planar waveguide optical splitter) is a key component in optical fiber communication networks and is widely used in optical fiber distribution systems such as FTTH (fiber to the home) and PON (passive optical network). Its main function is to evenly distribute the optical signal of a single optical fiber to multiple optical fibers to achieve optical signal splitting.
Compared with traditional fused taper splitters, PLC optical splitters have the advantages of high splitting accuracy, low insertion loss, and small size, and are particularly suitable for large-scale optical fiber network applications. With the popularization of optical fiber communication and the increase in bandwidth requirements, it is particularly important for people engaged in the field of optical communication to understand the role and application scenarios of PLC optical splitters. This article will take you to a comprehensive analysis of the working principle, advantages, and practical applications of PLC optical splitters.
Introduction to PLC Optical Splitters
PLC optical splitters, also known as planar waveguide optical splitters, are passive devices with multiple input and output ports that can evenly distribute one or two input optical signals to two or more output ports. This device is particularly suitable for passive optical networks such as FTTX, EPON, GPON, and BPON, and is used to connect central office equipment and terminal equipment to achieve efficient optical signal splitting. The main advantages of PLC optical splitters include:
- Even distribution of light: It can evenly distribute optical signals to up to 64 end users;
- Compact design: It is small in size and easy to install, and is commonly found in various junction boxes;
Cost-effectiveness: As the number of split channels increases, the cost-effectiveness becomes more and more significant, which is very suitable for the deployment of passive optical networks;
High optical splitting ratio: The optical splitting ratio is as high as 1:64, which is far higher than the traditional FBT optical splitters.
For more information on the difference between PLC optical splitters and FBT optical splitters and the selection guide, please refer to “Comparison of PLC Planar Waveguide Optical Splitter and FBT Fused Taper Optical Splitter”.
Manufacturing process of PLC optical splitters
PLC optical splitters are manufactured using advanced semiconductor processes. It consists of a PLC splitter chip and multiple optical waveguide arrays, which are coupled at both ends of the chip to connect the input and output optical fibers. Up to 64 splits can be realized on one chip. The PLC splitter chip is the core of the entire device and can provide a splitting ratio of 1:N or 2:N.
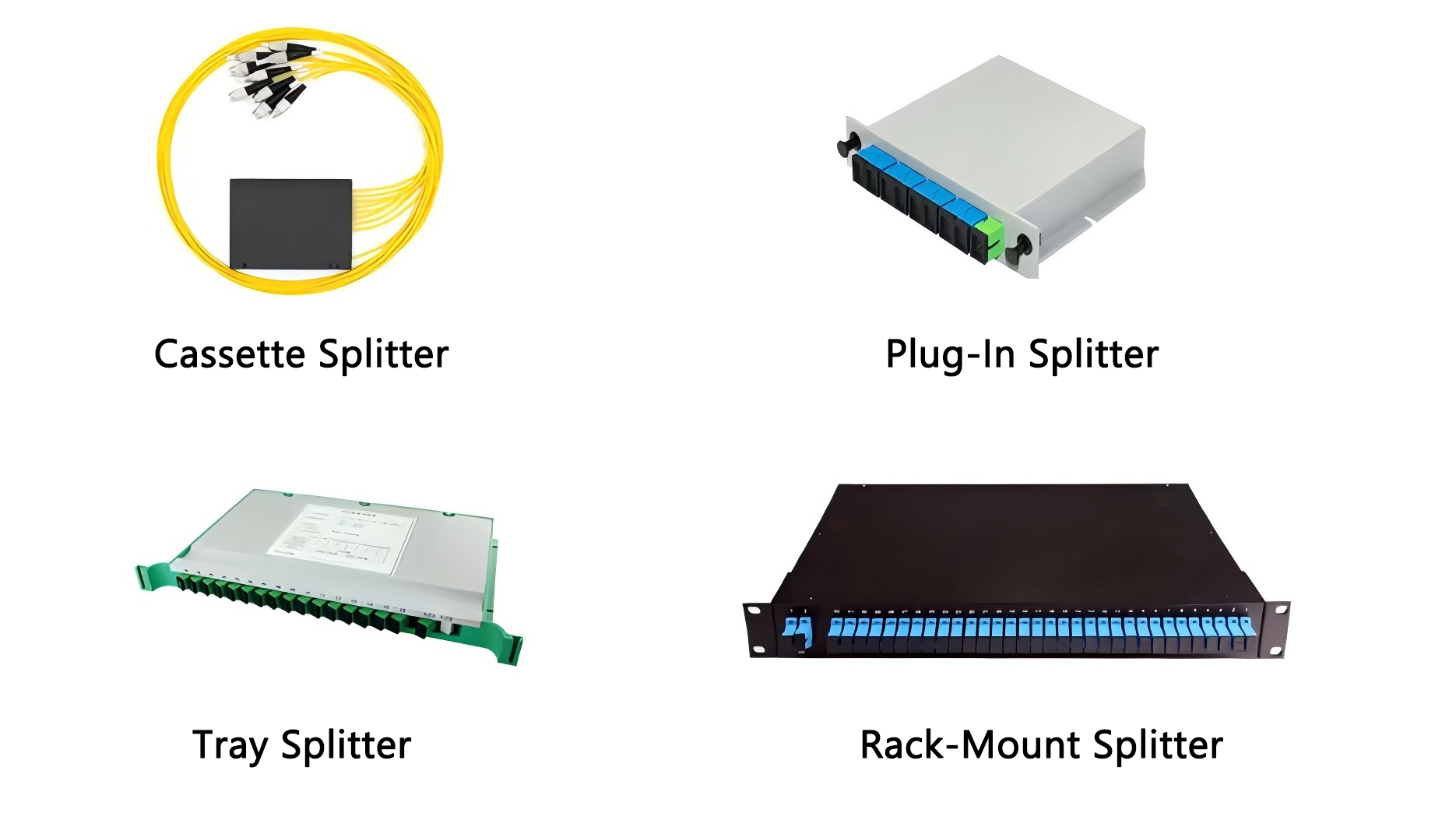
Depending on the number of chips, PLC optical splitters can be divided into two types: 1xN and 2xN, such as 1×4, 1×8, 1×16, 2×32, 2×64, etc. In addition, according to the different packaging types, PLC optical splitters can also be divided into bare fiber type, micro steel pipe type, ABS box type, with splitter type, tray type, rack type, LGX optical splitter and micro plug-in type to meet the connection needs of different scenarios.
Application of PLC optical splitters
In passive optical networks, PLC optical splitters are usually installed between optical line terminals (OLTs) and optical network units (ONUs) or optical network terminals (ONTs) near end users. Its input end is connected to the OLT fiber link in the central office (CO) to split the optical signal and transmit it to each end user.
There are two main ways to deploy PLC optical splitters: centralized distribution and cascade distribution. Centralized distribution is to install PLC optical splitters at a certain location between OLT and ONT, and then transmit the signals at the central office to the end users after centralized optical splitting. Cascade distribution involves more decentralized PLC splitters with a more complex structure, usually including primary optical splitting (such as 1:4 PLC optical splitter connected to OLT port) and secondary optical splitting (such as 1:8 PLC optical splitter connected to external terminal).
Through this article, you should have a comprehensive understanding of the basic working principle, main uses, and application scenarios of PLC optical splitters in optical fiber networks. With its efficient splitting performance and stable quality, PLC optical splitters play an indispensable role in modern optical fiber communication systems.
Whether in FTTH construction or PON network deployment, it is a core component to ensure efficient transmission of optical signals. With the continuous advancement of optical fiber technology, the application of PLC optical splitters will be more extensive and play a more important role in future optical communication networks. If you are planning or optimizing a fiber optic network, the reasonable selection and use of PLC optical splitters will bring you higher network performance and lower maintenance costs.