An optical circulator is a crucial device in the field of fiber optic communication, playing a significant role in enhancing the performance and flexibility of optical networks. This article delves into the functionality, types, applications, and advantages of optical circulators, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential component.
What is an Optical Circulator?
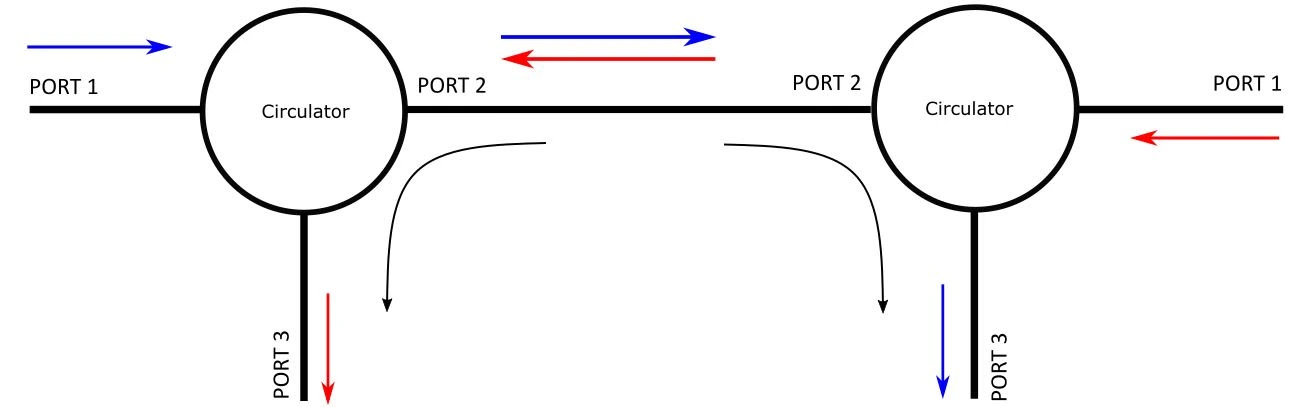
An optical circulator is a non-reciprocal, multi-port passive device that directs light from one port to the next in a unidirectional manner. Typically, it has three or four ports:
- Port 1: Entry point for the incoming light signal.
- Port 2: Intermediate port where the light signal from Port 1 is directed.
- Port 3: Final port where the light signal from Port 2 is redirected.
In a three-port circulator, the light entering Port 1 exits through Port 2, and the light entering Port 2 exits through Port 3. This unidirectional flow of light helps in managing signal routing efficiently in optical networks.
Types of Optical Circulators
Optical circulators can be broadly categorized based on their configurations and specific applications:
- Three-Port Circulators: The most common type, used for routing signals in a straightforward manner. They are typically employed in applications where simple signal flow is required.
- Four-Port Circulators: These offer additional flexibility by providing an extra port, making them suitable for more complex routing and signal management scenarios.
Applications of Optical Circulators
Optical circulators are employed in various applications due to their ability to control the direction of light signals precisely:
- Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) Systems: In WDM systems, optical circulators are used to separate and combine different wavelength channels, improving the efficiency of data transmission.
- Bi-Directional Transmission: They enable bi-directional transmission over a single fiber by separating the forward and backward propagating signals, enhancing the utilization of fiber infrastructure.
- Optical Add-Drop Multiplexers (OADM): Circulators are essential in OADMs for adding or dropping specific wavelength channels without affecting the remaining channels, facilitating dynamic and flexible network management.
- Optical Time-Domain Reflectometry (OTDR): In OTDR applications, circulators are used to direct the test signal and return signal to different ports, allowing precise measurement of fiber characteristics.
- Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) Sensors: They are used in FBG sensor systems to route signals and enhance the sensitivity and accuracy of the sensor readings.
Advantages of Optical Circulators
Optical circulators offer numerous advantages, making them indispensable in modern optical networks:
- High Isolation: They provide high isolation between ports, minimizing signal interference and crosstalk, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity.
- Low Insertion Loss: Circulators exhibit low insertion loss, ensuring that the signal strength remains robust as it passes through the device, thereby enhancing overall network performance.
- Compact and Robust Design: Their compact and robust design makes them suitable for deployment in various network environments, including space-constrained and harsh conditions.
- Enhanced Network Flexibility: By enabling efficient routing and management of light signals, circulators enhance the flexibility and scalability of optical networks, supporting the ever-increasing demand for bandwidth and connectivity.
Conclusion
Optical circulators, such as those provided by FiberLife, are vital components in the realm of fiber optic communication, facilitating efficient and flexible signal routing. Their ability to direct light in a unidirectional manner while maintaining high isolation and low insertion loss makes them essential for various applications, from WDM systems to OTDR and FBG sensors. As optical networks continue to evolve, the importance of optical circulators in ensuring robust and scalable network performance cannot be overstated. FiberLife continues to innovate and provide high-quality optical circulators that meet the demands of modern optical networks, ensuring reliable and efficient communication systems.