An optical splitter is distributes optical signals from one optical fiber to multiple optical fibers, thereby achieving parallel transmission of multiple signals. The PLC Splitters (Planar Light Waveguide Splitter) and FBT Splitters (Fused Taper Splitter) are the two most common types of optical fiber splitters. Although the functions of the two are very similar, both are used to distribute optical signals, there are significant differences in their structure, performance, cost, etc, making it difficult for many users to choose. The following will introduce the differences between them.
PLC Splitters Overview
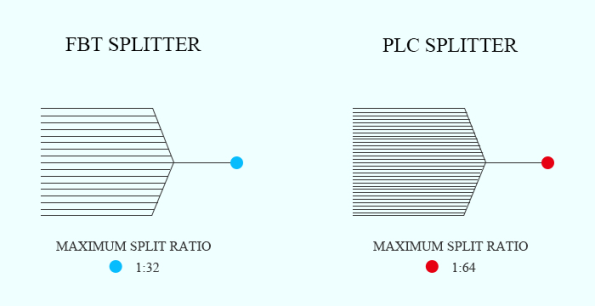
PLC Splitters (Planar Lightwave Circuit Splitter) is a fiber optic splitter based on optical waveguide technology. It uses optical waveguide to transmit the input optical signal through multiple paths to achieve signal distribution. In addition, PLC splitters provide a variety of splitting ratios, including 1×4, 1×8, 1×16, 1×32, 1×64, etc. PLC splitters are also divided into many types, such as bare PLC splitters, blockless PLC splitters, mini plug-in PLC splitters, etc.
Here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of PLC Splitters:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Low Insertion Loss | Higher Cost |
| Minimal signal loss during splitting. | More expensive due to complex design. |
| High Splitting Accuracy | Larger Size |
| Consistent splitting ratios across ports. | Takes up more space than FBT splitters. |
| Uniform Power Distribution | Longer Lead Time |
| Even signal distribution for stable performance. | Takes longer to manufacture and ship. |
| Wide Wavelength Range | Sensitive to Environment |
| Works well across various wavelengths. | Performance can be affected by extreme conditions. |
| High Reliability | |
| Stable and durable in different environments. |
FBT Splitters Overview
FBT Splitters (Fused Biconical Taper Splitter) is a traditional fiber splitter that heats and stretches two or more optical fibers to form a common “trumpet-shaped” connection structure. This structure distributes the input optical signal to multiple output ports. This method is relatively simple and low-cost.
Here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of FBT Splitters:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Low Cost | Higher Insertion Loss |
| More affordable due to simple design. | More signal loss during splitting. |
| Compact Size | Uneven Splitting |
| Smaller and easier to install. | Power distribution can be uneven. |
| Simple Manufacturing | Limited Wavelength Range |
| Easier and quicker to produce. | Typically works only at 1310nm and 1550nm. |
| Lower Reliability | |
| More prone to failure over time. |
Key Differences Between PLC Splitter and FBT Splitters
1. Wavelength Compatibility
The PLC Splitters supports a wide wavelength range (1260-1650nm), making it versatile for various optical systems, especially in long-distance communications and modern networks. In contrast, the FBT Splitters typically operates in a narrower wavelength range (1310nm and 1550nm), limiting its adaptability to certain network configurations and applications that require a broader wavelength spectrum.

2. Signal Distribution Accuracy
One of the main strengths of the PLC Splitters is its precise and consistent signal distribution, ensuring that each output port receives an equal share of light energy, making it highly reliable for large-scale networks. The FBT Splitters, however, does not provide the same level of accuracy. Its simpler manufacturing process can lead to some variation in signal strength, especially as the number of output ports increases.
3. Power Distribution Consistency
The PLC Splitters excels in providing highly uniform power distribution across all output ports, reducing the likelihood of some ports receiving much stronger or weaker signals. This is particularly important for maintaining network stability. On the other hand, the FBT Splitters often struggles with uneven power distribution, which can result in inconsistent signal quality, affecting the performance of connected devices.

4. Reliability and Durability
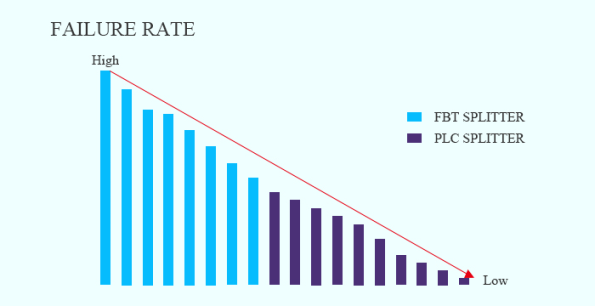
The PLC Splitters is known for its high reliability and long lifespan. Due to its advanced manufacturing technology and robust waveguide structure, it exhibits a lower failure rate and remains stable even in challenging conditions. Conversely, the FBT Splitters, with its simpler design, is more susceptible to failures and performance degradation over time, especially in harsh environments or under temperature fluctuations.
5. Performance Under Temperature Variations
The PLC Splitters is designed to perform consistently across a wide range of temperatures, from -40°C to 85°C, ensuring that it remains reliable even in extreme conditions. This makes it suitable for outdoor deployments or industrial settings. The FBT Splitters, however, is more sensitive to temperature changes, and its performance can degrade with fluctuations, leading to higher insertion losses and reduced efficiency in varying climates.
6. Cost Comparison
When it comes to cost, the PLC Splitters is more expensive due to its complex waveguide-based technology and higher manufacturing costs. This makes it a better choice for applications that require high precision and reliability. On the other hand, the FBT Splitters offers a more budget-friendly option. Its simpler design and manufacturing process make it a cost-effective solution for smaller or less demanding networks.
7. Physical Dimensions
In terms of physical size, the PLC Splitters is generally larger, thanks to the intricate technology involved in its construction. This may require more space for installation in certain setups, such as data centers or complex fiber networks. The FBT Splitters, being more compact and simpler in design, is easier to install in tight spaces, making it ideal for smaller-scale or residential networks where space is limited.
How to Choose the Right Splitter for Your Network
Requirement | Recommended Splitter |
|---|---|
| High precision, low loss, large-scale deployment | PLC Splitter |
| Budget-sensitive, short-distance applications | FBT Splitter |
| Need for wide wavelength range | PLC Splitter |
| Fixed wavelength applications | FBT Splitter |
| Harsh environmental conditions | PLC Splitter |
Conclusion
Although FBT Splitters and PLC Splitters are similar in appearance and size, their functions and specifications are quite different. In recent years, the emergence of PLC splitters has greatly improved splitter technology. Compared with traditional FBT splitters, PLC splitters are more reliable and stable. If you are currently looking for a splitter with high split count, small package size, low insertion loss and uniform power distribution, you should choose a PLC splitter instead of an FBT splitter.