OADM (Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer) is a technology widely used in optical fiber communication systems, which provides important support for the flexibility and efficiency of the network. In modern communication networks, the demand for data transmission is increasing. OADM helps optimize the use of bandwidth resources by allowing optical signals of specific wavelengths to be inserted or dropped in optical fiber links. Understanding the working principle of OADM can not only enable us to better grasp the core of optical communication technology, but also provide insights into the trend of future network development. Next, we will delve into the basic principles of OADM and its importance in practical applications.
01.What Is An OADM Optical Add/Dop Multiplexer?
Different optical channels enter and exit a single-mode optical fiber. Its main function is to selectively download or upload one or more wavelength channels without affecting the transmission of other wavelength channels. OADM equipment is one of the key devices in an all-optical network.
“Add” refers to the ability of the device to add one or more new wavelength channels to an existing multi-wavelength WDM signal, while “Drop” refers to downloading or removing one or more channels leading to local signals, passing these signals to another network path, and not affecting the transmission of other existing wavelength channels along the original route.
02.Functions Of An Optical Add/drop Multiplexer
The traditional OADM consists of an optical multiplexer, an optical demultiplexer, and a reconstruction method between them, that is, a method for reconstructing the path between an optical demultiplexer, an optical multiplexer, and a series of ports for adding and dropping signals.
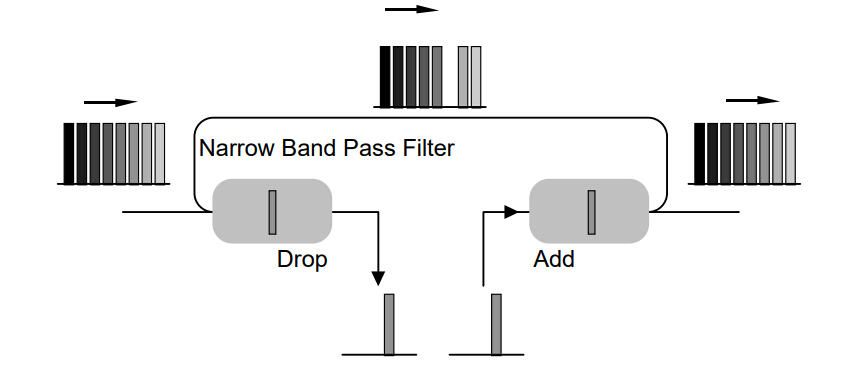
The add/drop unit is the core implementation function of the OADM, which can selectively add or drop a wavelength signal from multiple wavelengths transmitted, or only pass a wavelength signal, but does not affect the transmission of other wavelength channels. MUX multiplexes the wavelength channels and transmits them to an output fiber, while DEMUX separates the wavelengths on the input fiber and transmits them to the port. This reconstruction process can be achieved through fiber jumpers or optical switches.
The specific working process of OADM is as follows: the WDM signal input from the line contains four wavelength channels from λ1 to λ4, among which, according to business needs, the λ2(B) and λ4(D) wavelength channels are selectively downloaded (Drop) to the local area, and the different local λ2(E) and λ4(F) wavelength channels are added accordingly, and multiplexed with other wavelength channels not related to the local area, and then output from the line output end of OADM.
03.Types Of Optical Add/drop Multiplexers (FOADM, TOADM)
According to the flexibility of adding and dropping wavelengths, OADM can be divided into fixed wavelength OADM (FOADM) and reconfigurable OADM (ROADM). FOADM is usually used in fixed communication networks, and its wavelength channels are pre-set and cannot be changed. TOADM is more flexible, and its wavelength channels can be adjusted to any wavelength, with strong adaptability.
FOADM (Fixed Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer) can only add and drop channels with fixed wavelengths. Compared with ROADM, it cannot be adjusted dynamically.
The figure shows a simple schematic diagram of FOADM. First, demux separates all wavelengths, drops the specified wavelength to the local node, and the remaining wavelengths pass through the node. At the same time, another local specified wavelength is added to the channel, and other wavelengths driven to the next node through the Mux. FOADM means that you cannot temporarily change the wavelength of the add/drop channel because it is fixed.
Common FOADM can be divided into three types: thin film filter type (TFF type), fiber Bragg grating (FBG type) and integrated planar array waveguide grating (AWG type). In terms of frequency band, FOADM can be divided into DWDM OADM and CWDM OADM.
ROADM (Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer) is a device or equipment used in dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) systems. Its function is to dynamically add or drop service wavelengths through remote reconfiguration. In other words, in the middle of the line, the wavelengths of the added and dropped services can be arbitrarily assigned as needed to achieve flexible scheduling of services. WSS (optical wavelength selection switch) is usually selected to implement the addition and drop multiplexing of any single-wavelength or multi-wavelength signal.
In order to achieve non-blocking wavelength switching and up/downloading, the new generation of ROADM nodes are required to have the characteristics of colorless, directionless and contention-less, which is CDC-ROADM. The advantage of CDC-ROADM is that it can upload and download any frequency band on any port, and at the same time solves the problem that the same frequency band cannot be placed on the same path, greatly reducing the difficulty and efficiency of fault recovery. ROADM nodes are usually composed of wavelength selective switches (WSS) and other modules. The CDC (colorless, non-directional and non-contention) function depends on the structure of the ROADM node, while the flexible bandwidth function depends on the key module WSS. Unlike fixed optical add-drop multiplexers, ROADM allows online reconfiguration without affecting traffic.
Based on cost considerations, the existing metropolitan area network is mainly based on CWDM and FOADM (fixed optical fork multiplexer) technologies. In order to upgrade the network, DWDM and ROADM (reconfigurable optical fork multiplexer) technologies previously used in backbone networks are expected to be sunk to metropolitan area networks.
04.Application Of OADM
Metropolitan area network MAN
Due to the flexibility of OADM, it is mainly used in MAN (metropolitan area network). Its networking is flexible, easy to upgrade and expand the scale of the network, and it is an ideal multi-service transmission platform for metropolitan area network applications. In the DWDM metropolitan area network structure, OADM (optical add-drop multiplexer) is the most critical component, and a large number of OADMs are required. Its function is to flexibly add separation wavelengths in the DWDM loop.
Optical Cross-Connect OXC
OADM is a key product of the all-optical network. It does not require photoelectric conversion, is not affected by electronic bottlenecks, can transparently transmit data, and is flexible and reliable in networking.
With the continuous demand for information and the rapid development of information technology, network communication has become an indispensable part, and OADM (Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer), as a core device in the optical fiber communication system, provides important support for network communication. If you need to learn more about OADM optical add-drop multiplexer product information, please visit the official website of Fiber-Life.com. Thank you for your support!