When dealing with Optical Transport Network (OTN), there are two main types of Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) systems: Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) and Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM). Both technologies are used to increase the bandwidth of fiber networks by combining optical signals of different wavelengths on a single strand of fiber. But what are the key differences between CWDM and DWDM?
Introduction to WDM, CWDM, and DWDM
To understand the differences between CWDM and DWDM, it is essential to first grasp the concept of WDM.
What is WDM?
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a technology that allows for the transmission of multiple data streams simultaneously over a single optical fiber network. This maximizes fiber utilization and helps optimize network investments.
What are CWDM and DWDM?
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) and DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) are two technologies developed based on WDM. CWDM is a flexible technology suitable for most fiber networks, typically used in point-to-point topologies within enterprise networks and telecom access networks. DWDM, on the other hand, is often deployed in metropolitan networks, data center interconnections, and financial services networks, usually in a ring topology.
Key Differences Between CWDM and DWDM
Channel Spacing
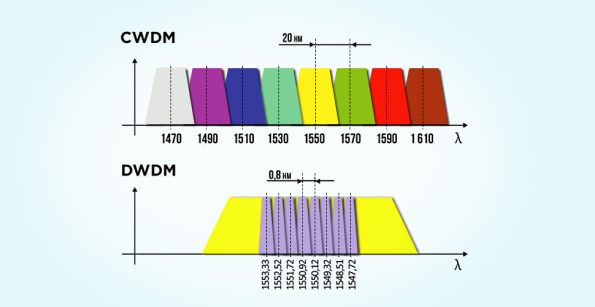
Channel spacing refers to the nominal difference in frequency or wavelength between two adjacent optical channels. CWDM has a wider spacing, capable of transporting up to 18 wavelengths with 20nm spacing in the spectrum grid from 1271nm to 1611nm. DWDM, however, can carry 40, 80, or up to 160 wavelengths with much narrower spacing of 0.8/0.4nm (100 GHz/50 GHz grid), covering wavelengths from 1525nm to 1565nm (C band) and 1570nm to 1610nm (L band).
Transmission Distance
CWDM has a maximum reach of about 160 km, while DWDM can cover much longer distances due to its highly integrated wavelengths during light transmission. Amplified DWDM systems can extend even further.
Modulation Laser
CWDM systems use uncooled lasers, whereas DWDM systems use cooled lasers with temperature tuning. The cooling laser in DWDM ensures better performance, higher safety, and a longer lifespan but consumes more power compared to the uncooled laser used by CWDM systems.
Bandwidth
CWDM carries less bandwidth per channel than DWDM. CWDM transceivers can reach 100 Gbps, with integrated components pushing over 1 Tbps, whereas DWDM transceivers can currently reach up to 400 Gbps.
Applications
CWDM is widely used in cable TV networks and transceivers like GBIC and SFP CWDM optics, providing standardized wavelengths for efficient data transmission. It is ideal for FTTP (Fiber to the Premises) as it requires no power and uses passive optical components. DWDM, used extensively in telecom and cable networks, is crucial for long-distance, high-bandwidth secure applications. It boosts bandwidth in core and metro networks and supports high-throughput data centers.
Cost
CWDM systems are generally more cost-effective than DWDM systems due to the simpler technology and the use of uncooled lasers. However, the price difference between CWDM transceivers and DWDM transceivers has narrowed due to the popularization of DWDM.
Advantages and Disadvantages
CWDM Advantages:
- Lower power consumption
- Smaller space requirements
- Can use single-mode fiber (SMF) or multimode fiber (MMF)
- Can use LEDs or lasers for power
- Larger individual payloads per channel
- Smaller and cheaper wave filters
- Cost savings on start-up and expansion
CWDM Disadvantages:
- Less capacity than DWDM
- Shorter range
- Requires regeneration instead of amplification
- Not carrier-class in terms of operations, administration, and management (OAM) functions
DWDM Advantages:
- Maximum capacity system available
- Maximum distance capability with Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFA)
- Fewer repeater/amplifier sites required
- Pay-as-you-grow expansion model
- Mature OAM systems
DWDM Disadvantages:
- Requires more space
- Consumes more power
- Needs high accuracy lasers and wave filters
- Expensive EDFAs for amplifiers
- Higher start-up costs compared to CWDM systems
Conclusion
The rising need for bandwidth has propelled DWDM’s popularity, especially for high data rates and long distances. However, CWDM remains advantageous for lower data rates and shorter distances due to its cost-effectiveness. Both CWDM and DWDM will continue to serve distinct roles in the OTN network, complementing each other. FiberLife offers a comprehensive range of CWDM and DWDM products to meet diverse networking needs, ensuring the right fit for any project.
For more information, visit the FiberLife community blog on WDM technology and explore their extensive product offerings.