In today’s competitive landscape, telecommunications, cable, and data providers strive to deliver high-quality services while adopting state-of-the-art technologies to ensure data integrity and user segregation. Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) stands out as a cost-effective and forward-looking solution. This guide delves into DWDM technology, components, working principles, and benefits, helping you make the right decisions for your business.
Introduction to DWDM Technology
According to Dell’Oro, DWDM is projected to achieve a compound annual growth rate of 3%, reaching $18 billion by 2026.
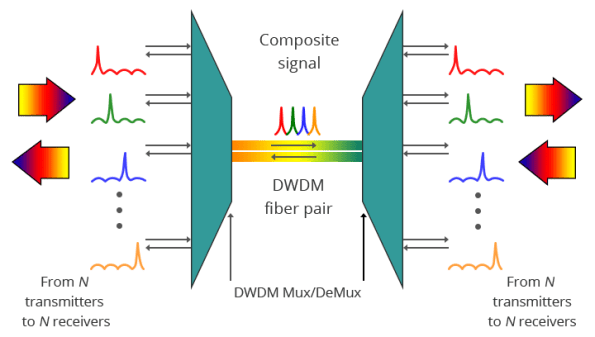
DWDM technology is an extension of optical networking and is designed to maximize the capacity and efficiency of fiber-optic networks. It achieves this by allowing multiple data streams to be transmitted simultaneously over a single optical fiber using different wavelengths of light. DWDM is a subset of wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) that typically uses the spectrum band within 1530nm and 1625nm, or more commonly the C-band and L-band, to input 40, 88, 96, or even 160 wavelengths, or channels, onto a single strand of fiber optic cable.
DWDM got its name from using tighter wavelength spacing (dense) to fit more channels, with each channel being only about 0.8nm wide. This is opposed to its WDM sibling, CWDM, which uses a wider range of frequencies, with each channel spread farther apart. With a CWDM channel being 20nm wide, the high number of channels available to DWDM means it can cram much more data into the cable. By adopting high-quality AAWG Gaussian technology, FiberLife DWDM Mux Demux provides low insertion loss (3.5dB typical) and high reliability. With the upgraded structure, these DWDM components offer easier installation.
DWDM System Components
A DWDM system generally consists of five main components: DWDM Mux/DeMux, DWDM transceivers, Optical Add/Drop Multiplexers (OADMs), optical amplifiers, and transponders (Wavelength Converters).
DWDM Mux/DeMux
DWDM Mux/DeMux is integral to DWDM systems, serving as a critical passive optical component facilitating the simultaneous transmission of multiple data channels over a single fiber. The Mux combines diverse wavelengths onto the fiber, adhering to the ITU grid for standardized channel spacing. At the receiving end, the Demux separates these wavelengths, enabling the independent processing of individual data streams. Its passive nature ensures low insertion loss, and advanced configurations may include add-drop functionality for increased network flexibility. Typically, Mux and Demux components are contained in a single enclosure and operate without requiring an external power source.
DWDM Transceivers
A DWDM transceiver is crucial in fiber-optic communication systems, enabling the simultaneous transmission and reception of multiple data signals at specific wavelengths over a single optical fiber. It comprises a transmitter that converts electrical signals to designated wavelengths and a receiver that detects incoming signals at those wavelengths. DWDM transceivers leverage DWDM technology to multiplex different wavelengths or several optical signals onto a single fiber, saving valuable fiber resources. They come in various types supporting transmission rates from 1 Gbit/s to 400 Gbit/s, including DWDM SFP, SFP+, SFP28, and QSFP28 transceivers.
Optical Add/Drop Multiplexers (OADMs)
OADMs add or drop specific wavelengths from the multiplexed signal, enabling the insertion or extraction of channels at various points along the network. Reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexers (ROADMs) allow the routing and rerouting of any wavelength in any direction, enhancing network flexibility and performance. FiberLife’s ROADM utilizes advanced wavelength-selective switch (WSS) technology to enable full CDC-F (colorless, directionless, and contentionless) system configuration, simplifying installation and scalability.
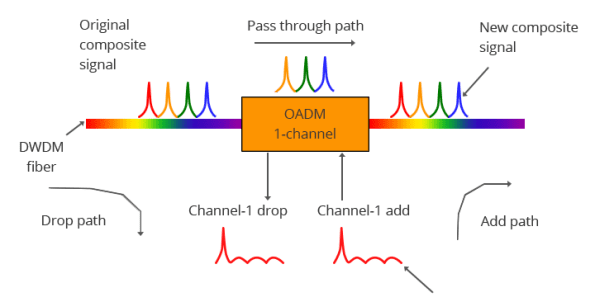
Optical Amplifiers
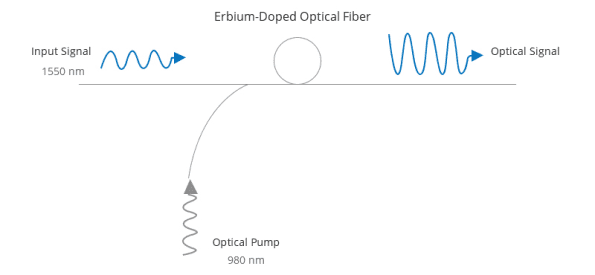
Optical amplifiers boost the amplitude or add gain to optical signals passing through a fiber by directly stimulating the photons of the signal with extra energy. They are crucial for DWDM systems, extending the transmission distance. Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs) are the most commonly used type of in-fiber optical amplifiers, essential for DWDM applications. Other types include CATV EDFA, SDH EDFA, EYDFA, and Raman amplifiers.
Transponders (Wavelength Converters)
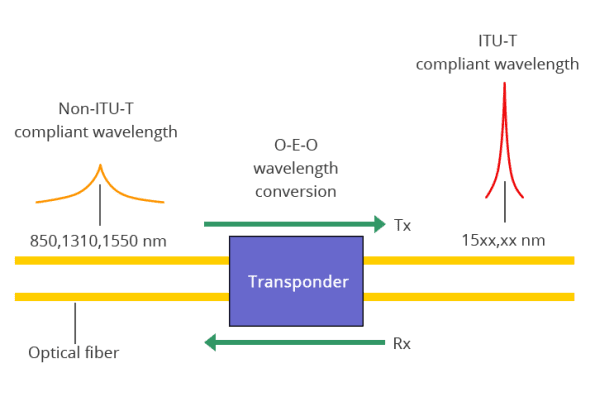
Transponders convert optical signals from one incoming wavelength to another outgoing wavelength suitable for DWDM applications. They perform Optical-Electrical-Optical (O-E-O) conversion, often called OEO converters. Transponders map the client optical signal to a DWDM wavelength and send it to the multiplexer. They support transmission rates from 10 to 400 Gbps and come with different module ports.
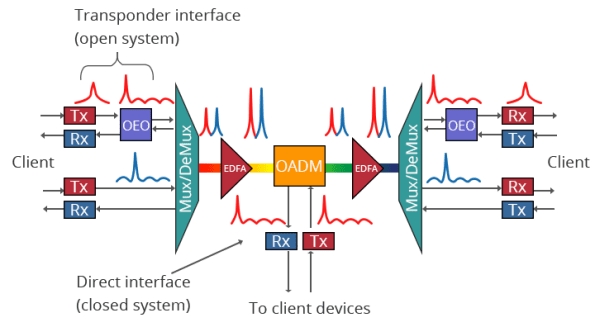
How DWDM System Components Work Together with DWDM Technology?
- Data Stream Input: The data stream enters and is input into the transponder.
- Wavelength Mapping: The transponder maps the signal to a DWDM wavelength and sends it to the multiplexer (Mux) to consolidate the optical signal.
- Signal Boosting: As the signal leaves the multiplexer, optical amplifiers boost it for long-distance travel.
- Add/Drop Functionality: Along the way, OADMs can add and remove bitstreams of specific wavelengths. Additional amplifiers may be used to extend the signal’s distance further.
- Signal Reception: The signal arrives and gets de-multiplexed (DeMux) into individual DWDM wavelengths, which are then passed through the transponder to be converted into the corresponding signals for routing to their final destination.
Benefits of DWDM
DWDM transmits large amounts of data over long distances, making it ideal for long-haul transmission. It can be integrated with existing fiber optic cables, allowing providers to increase data capacity as optical technology improves. As a cost-effective solution, DWDM reduces the need for extensive new fiber installations. Additionally, it is protocol and bitrate independent, capable of carrying various data types—voice, video, and text—across a single fiber optic cable without interference, benefiting providers that offer multiple services.
FiberLife DWDM Solution
FiberLife provides efficient and easy-to-use 100G DWDM PAM4 solutions with the DCP series, featuring EDFA, MUX/DEMUX, and 100G DWDM PAM4 modules. These solutions enable swift deployment and stable long-range optical links, reducing costs and operational hassle. With zero-touch provisioning and automatic management, they optimize operations and facilitate maintenance, making them ideal for enhancing enterprise productivity and efficiency.