In the realm of optical communication, precision and efficiency are paramount. Among the various components that ensure high-quality signal transmission, fiber collimators stand out for their essential role in aligning and directing light. This blog delves into the fundamentals of fiber collimators, their working principles, applications, and the advantages they bring to the optical communication landscape.
What is a Fiber Collimator?
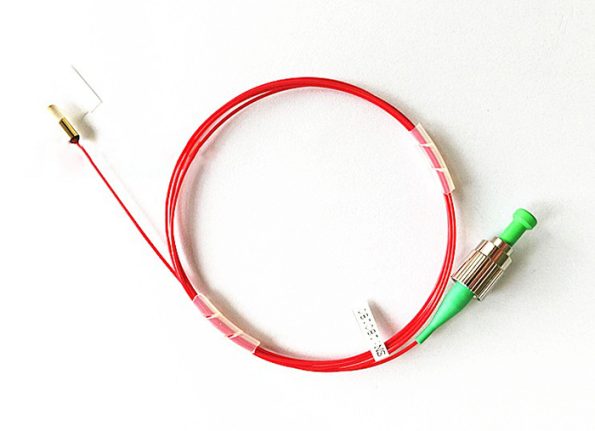
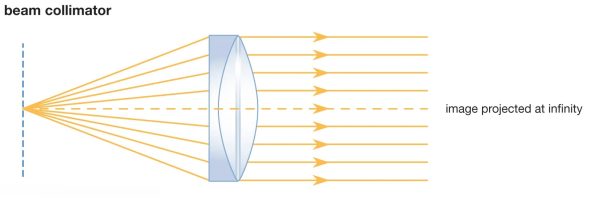
A fiber collimator is an optical device used to align light into a parallel beam. It consists of an optical fiber and a lens, where the fiber guides the light and the lens collimates it. The primary purpose of a fiber collimator is to couple light efficiently from a fiber into free space or another optical component, ensuring minimal divergence and optimal alignment.
Working Principle
The working principle of a fiber collimator involves the precise alignment of the fiber end and the lens to produce a collimated beam of light. Here’s a step-by-step outline of how it works:
- Light Emission: Light exits the optical fiber’s core.
- Lens Alignment: A lens, often a graded-index (GRIN) lens or an aspheric lens, is positioned to collect and collimates the emitted light.
- Collimated Beam: The lens adjusts the light into a parallel beam, minimizing divergence and maintaining the beam’s quality over a distance.
Types of Fiber Collimators
Fiber collimators come in various designs, each suited to specific applications and performance requirements:
- Fixed Focus Collimators: These have a fixed focal length and are typically used in applications where the distance between components is constant.
- Adjustable Focus Collimators: These allow for adjustments in the focal length, providing flexibility in aligning and optimizing the beam.
- Single-Mode Collimators: Designed for single-mode fibers, they offer high precision and low loss for applications requiring exact alignment.
- Multi-Mode Collimators: Suitable for multi-mode fibers, they handle higher power levels and are used in applications where alignment tolerances are less stringent.
Applications of Fiber Collimators
Fiber collimators are integral to various optical systems, enhancing performance and efficiency in multiple applications:
- Telecommunications: Used in optical transmitters and receivers to couple light efficiently, improving signal integrity and reducing losses.
- Fiber Lasers: Essential for beam shaping and directing in fiber laser systems, ensuring high-quality laser output.
- Optical Sensing: Employed in sensors to align and direct light, increasing the accuracy and sensitivity of measurements.
- Medical Devices: Utilized in medical imaging and diagnostic equipment for precise light delivery and collection.
Advantages of Fiber Collimators
Fiber collimators offer several benefits that make them indispensable in optical communication and beyond:
- High Precision: They ensure accurate alignment of light, crucial for high-performance optical systems.
- Low Loss: By minimizing beam divergence, fiber collimators reduce signal loss and improve transmission efficiency.
- Versatility: Available in various designs, they can be tailored to meet specific application requirements.
- Compact Design: Their small size allows integration into a wide range of devices and systems without adding bulk.
Conclusion
Fiber collimators play a critical role in the precise alignment and efficient transmission of light in optical systems. Their ability to produce collimated beams with minimal loss and high precision makes them essential components in telecommunications, fiber lasers, optical sensing, and medical devices. As optical communication technology continues to advance, the demand for high-quality fiber collimators, especially those from Fiber-Life, will only grow, driving further innovation and optimization in this vital field.