Investing in the right fiber optic cables for transceivers is crucial for optimizing data transmission. This guide will walk you through essential considerations to ensure a worthwhile investment.
Content:
Fiber optic transceivers, often referred to as optical modules, are sophisticated devices that facilitate the transmission and reception of data via optical fibers, replacing the need for traditional electrical wires. Before selecting the appropriate optic cables for these transceivers, it’s imperative to understand the basics of fiber optic cables.

Basics of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are conduits for light, transmitting data in the form of light pulses through highly pure glass or plastic fibers. Their popularity in telecommunications and Ethernet networking is attributed to their ability to deliver high-speed data transmission over long distances.
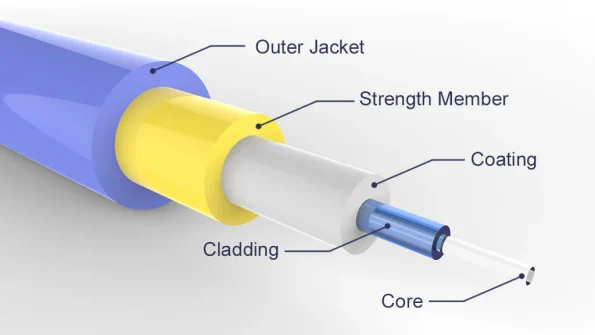
At the heart of these cables lies a slender glass tube, the core, which carries the light pulses generated by a light-emitting diode or laser. The core can be single-mode or multimode, each with distinct diameters. Surrounding the core is the cladding, a thin glass layer that protects the core and reflects light back into it, ensuring that light waves travel the full length of the fiber.
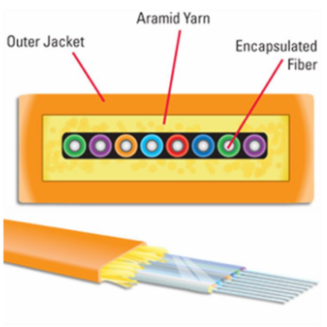
An additional protective layer, known as the primary coating or buffer, shields the fiber from excessive bending, absorbs shocks, and reinforces the core. Strengthening members, such as gel-filled sleeves or Kevlar strands, further safeguard the cable from crushing or pulling forces during installation.
The outermost layer, the cable jacket, provides the final layer of protection. It not only strengthens the cable but also safeguards the core conductor. The jacket is color-coded, indicating the cable’s rating and the type of optical fibers it contains.
Factors to Consider When Purchasing Fiber Optic Cables
- Bend Radius: While fiber cables are generally easy to install, it is vital to maintain their minimum bend radius during installation. Exceeding this bend radius can result in cable breakage or increased signal attenuation. It is reassuring to know that if the cable elements remain intact, the attenuation should revert to normal once the bend is corrected.
- Distance and Network Speed: Historically, multimode fibers were the preferred choice due to their lower cost compared to single-mode fibers. However, with the cost difference now negligible, the decision can be based on the network’s speed and connection distance requirements. Multimode fibers are ideal for transmitting large volumes of data over shorter distances, whereas single-mode fibers are better suited for applications where transmission distance and speed are paramount. The performance range of multimode fibers is also highly dependent on the cable’s OM rating.
When faced with numerous factors that influence the purchase decision, it is advisable to consult with experts. At FiberLife, we have assisted numerous businesses in making strategic investments in future-proof networks that foster growth and innovation.
Our comprehensive range, designed to enhance connectivity, encompasses everything from connector systems to joints, cables, attenuators, and other top-tier products that ensure exceptional performance across all networks.
Our offerings include fiber patch cables, optical amplifiers, MPO and MTP cables, LC and SC cables, fiber optic adapters, fiber quick connections, FBT couplers, PLC splitters, and much more. Contact us to discover how we can empower your business to stay at the forefront of networking technology with our world-class solutions.