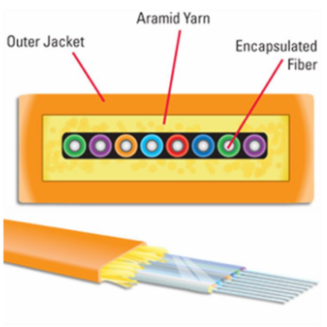
When designing a fiber optic network, it’s crucial to understand the various cable options available. The specific demands of your network will dictate the optimal cable choice, but having a clear understanding of the different fiber cables is essential for making an informed decision. While a comprehensive list of design differences could fill several volumes, this concise guide will outline the key characteristics of OS2, OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5 Fiber Optic Cables.
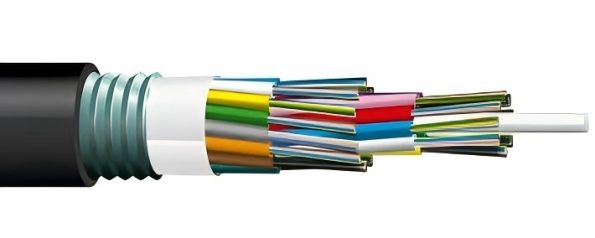
OS vs OM Fiber Optic Cables
The primary distinction to grasp is between OS and OM cables. In the simplest terms, OS cables are singlemode fibers, while OM cables are multimode fibers. If this distinction is clear enough, you can proceed to the next section.
For those seeking more depth, there are several key design differences between these cable types, primarily related to their single- or multimode functionality. OS cables feature significantly thinner cores than OM cables. For instance, an OS cable like OS2 typically has a 9-micron core, whereas OM cables can exceed 100 microns. Additionally, OM cables are designed for shorter distances and to work with more cost-effective transmission components.
OM Fiber Optic Cables Varieties
If multimode fiber is the appropriate choice for your network, there are still critical decisions to make. The cables are available in five distinct designs: OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5. OM1, despite being an older and slower option, remains common in modern applications due to its cost efficiency for short distances. It uses a 62.5/125-micron core. The other four designs utilize a 50/125-micron core.

Transmission Differences
A significant difference lies in transmission technology. OM1 and OM2 cables use LED transmitters, which are cost-effective but limit bandwidth, with top speeds of around 1Gbps. In contrast, OM3, OM4, and OM5 cables employ laser-optimized multimode (LOMMF) transmission, which is more expensive but enables higher bandwidths. These cables can achieve speeds up to 10Gbps (OM3), 40Gbps (OM4), and 100Gbps (OM5).
While there are subtler differences among these cables, the above distinctions cover the majority of their applications.
OS Fiber Optic Cables Options
Regarding OS cables, they come in OS1 and OS2 configurations. OS1 is somewhat outdated, designed for distances less than 2km with a top transmission speed of 10Gbps. For such ranges, OM designs are often more cost-effective. OS2 is the standard for long-range networking, capable of carrying signals up to 200 km and achieving transmission rates exceeding 10Gbps.
The purpose of OS2 fiber cabling is to handle tasks best suited to singlemode fiber optics, making it the go-to choice for long-range, high-speed applications.
Simplicity and Clarity
We advocate for simplicity and straightforwardness. In almost every case, the best cable is the one that meets your distance and speed requirements at the lowest possible cost.
Still uncertain about the right fiber cable for your data center or project? Engage with one of our Fiber Cable experts:sales@fiber-life.com, and they can assist you in making the right choice and guide you in the right direction.
Don’t forget to explore our new Fiber-Life LSZH Fiber cables today.