In the ever-evolving world of telecommunications, fiber optic networks stand as a cornerstone, enabling the rapid and reliable transmission of data. At the heart of these networks are fiber splitters, critical components that ensure efficient data distribution. This blog post will delve into the intricacies of fiber splitters, their types, applications, and the advantages they bring to modern communication systems.
What is a Fiber Splitter?
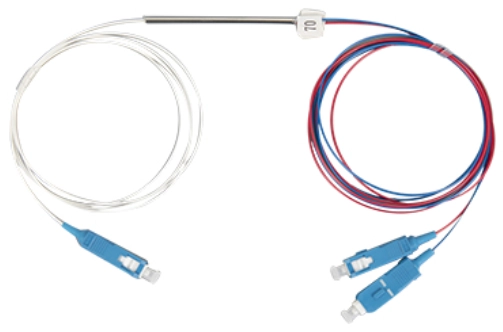
A fiber splitter, also known as a beam splitter, is a passive optical device that splits an optical signal into multiple signals. It is a crucial component in Passive Optical Networks (PON) and Fiber to the Home (FTTH) deployments. By dividing a single optical signal into multiple signals, fiber splitters facilitate the distribution of data from a central office to numerous end-users, maximizing the efficiency of the fiber optic network.
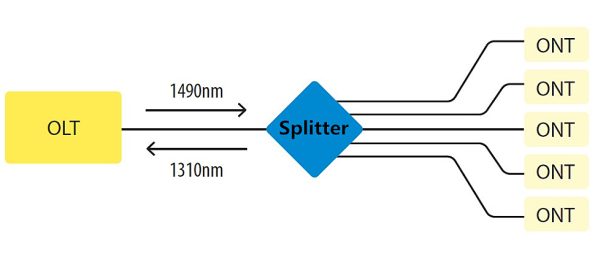
Types of Fiber Splitters
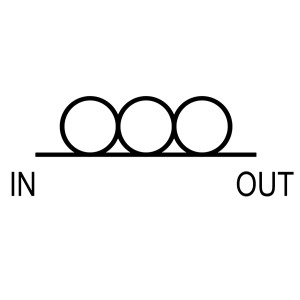
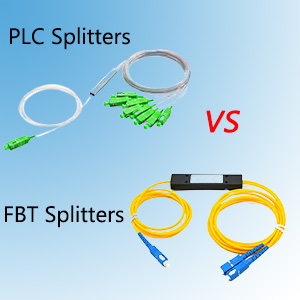
Fiber splitters are broadly categorized into two types: FBT (Fused Biconical Taper) splitters and PLC (Planar Lightwave Circuit) splitters.
- Construction: Made by fusing and tapering two or more fibers together.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, suitable for networks with low split ratios (1×2, 1×4).
- Disadvantages: Limited to low split ratios, less uniform distribution of light, sensitive to wavelength variations.
- Construction: Utilize photolithographic techniques to create a circuit on a silica glass substrate.
- Advantages: High reliability, compact size, uniform light distribution, suitable for high split ratios (1×16, 1×32, 1×64).
- Disadvantages: Higher cost compared to FBT splitters.
Applications of Fiber Splitters
Fiber splitters are integral to various applications in fiber optic networks, including:
- FTTH Networks: Delivering high-speed internet to homes by splitting the signal from a central office to multiple residences.
- Cable TV: Distributing television signals to numerous subscribers.
- Data Centers: Facilitating data transmission between servers and storage devices.
- Telecommunication Networks: Enhancing the efficiency of signal distribution in large-scale communication networks.
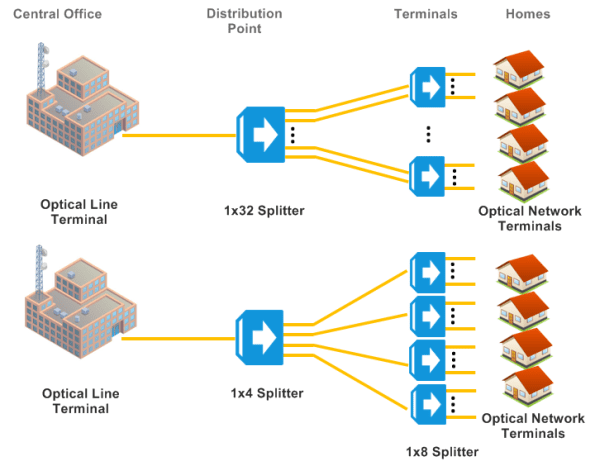
Advantages of Using Fiber Splitters
- Cost-Efficiency: By splitting a single optical signal into multiple outputs, fiber splitters reduce the need for additional network infrastructure, leading to significant cost savings.
- Scalability: Fiber splitters enable the expansion of fiber optic networks to accommodate more users without requiring extensive modifications.
- Reliability: High-quality fiber splitters, especially PLC splitters, offer reliable performance and uniform signal distribution, ensuring consistent network quality.
- Space-Saving: Compact designs of PLC splitters save space in network installations, making them ideal for high-density applications.
Conclusion
Fiber splitters are indispensable components in modern fiber optic networks, driving the efficient distribution of data to multiple end-users. Understanding the types, applications, and benefits of fiber splitters is crucial for optimizing network performance and ensuring seamless communication. As the demand for high-speed internet and data services continues to grow, the role of fiber splitters, such as those offered by Fiber-Life, in expanding and enhancing network capabilities becomes increasingly significant. Fiber-Life‘s high-quality fiber splitters ensure reliable performance, making them an excellent choice for modern communication systems.