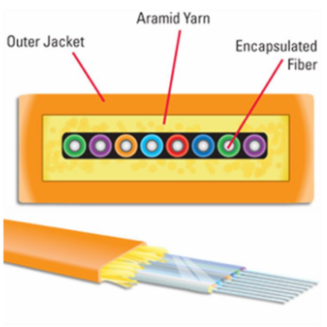
Common Problems and Solutions for MPO Fiber Patch Cables
MPO fiber patch cables are widely used in modern high-density data centers and telecommunication networks due to their ability to transmit multiple optical signals in a compact space. However, as MPO connectors become more prevalent, several common issues have surfaced. Fiber-LIFE will discuss these problems and their solutions in detail to help you better manage and maintain your MPO fiber network.
Polarity Management Issues
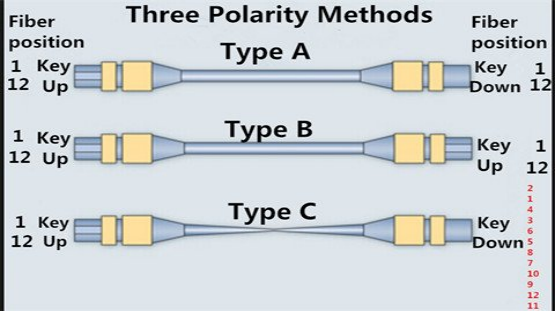
Polarity management is crucial to ensure that optical signals are correctly transmitted from the transmitter to the receiver. However, due to the various polarity configurations of MPO connectors (such as Type A, Type B, and Type C), polarity errors can easily occur during installation and maintenance, leading to signal transmission failures. To address polarity management issues, it is essential to have an in-depth understanding of the different MPO polarity types and their uses.
- Type A: Straight-through polarity.
- Type B: Cross-over polarity.
- Type C: Pairwise flip polarity.
Familiarizing yourself with each type’s connection method and applicable scenarios is the foundation for avoiding polarity errors. Additionally, clearly labeling each MPO fiber patch cable and recording its polarity information during installation and maintenance can prevent confusion. Using polarity testers to check each cable ensures correct polarity and can effectively prevent installation errors. These measures can significantly reduce the occurrence of polarity errors and ensure the normal operation of the fiber network.
Connector End-Face Contamination
Contamination of connector end-faces (such as dust, dirt, or scratches) is one of the main causes of optical signal transmission problems. Even small contaminants can significantly increase insertion loss and reflection loss. To address connector end-face contamination, it is necessary to regularly inspect the cleanliness of connector end-faces using an optical microscope or automated inspection equipment. This inspection helps identify and locate contaminants. Additionally, using specialized fiber cleaning tools, such as dry cleaning sticks or wet cleaning pens, thoroughly clean the connector end-face. Typically, a dry clean followed by a wet clean, ensuring a final dry wipe, is recommended. After cleaning, re-inspect with a microscope to ensure the end-face is completely clean and free of contamination. Maintaining clean connector end-faces can significantly reduce insertion and reflection losses, improving the performance of the fiber network.
Connector Misalignment
Connector misalignment refers to the failure of two optical fiber cores to align accurately, leading to high reflection and insertion loss. Common causes include incomplete insertion of connectors, poor end-face geometry, or guide pin failure. To resolve connector misalignment issues, ensure MPO connectors are fully aligned and inserted with appropriate force during installation. Additionally, selecting high-quality MPO connectors is crucial as they typically have better end-face geometry and mechanical performance, reducing the likelihood of misalignment. Regularly inspecting the physical condition of connectors and promptly replacing faulty connectors can effectively prevent and correct misalignment problems. These measures ensure the connection quality of the fiber network and reduce signal loss.
Cable Faults
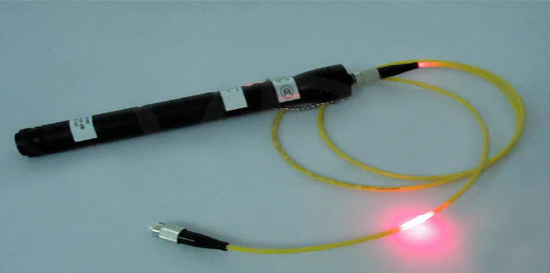
Cable faults such as excessive bending, pulling, or breaking can lead to signal attenuation or even interruption. Excessively small bending radii, particularly during installation, can cause permanent damage to the fiber. To address cable faults, strictly adhere to the bending radius requirements for optical fibers. During installation and cabling, ensure the bending radius of the fiber is no less than its minimum bending radius (typically 20 times the diameter of the cable). Using a visual fault locator (VFL) is a simple and effective method for locating faults. VFL emits a visible red laser, allowing the identification of breaks or severe bends by observing bright spots in the fiber. For faults that cannot be precisely located with a VFL, an optical time-domain reflectometer (OTDR) can be used. OTDR accurately measures the loss and reflection events in the fiber link, helping to locate hidden faults. By adhering to bending radius requirements and using professional fault detection tools, cable faults can be effectively reduced, improving the reliability of the fiber network.
Insertion Loss Exceeding Budget
Insertion loss refers to the loss of optical signal energy during transmission, typically measured in dB. If insertion loss exceeds the budget, it can lead to signal attenuation and affect network performance. To address insertion loss exceeding the budget, accurately calculate the insertion loss budget during the network design phase based on fiber type, link length, and the number of connection points. Detailed design planning can estimate and control the total loss of the fiber link. After installation, use an optical power meter to test the insertion loss of each fiber link, ensuring the actual loss is within the budget. Additionally, during design and installation, minimize the number of connection points and connectors in the fiber link to reduce insertion loss. These methods effectively control insertion loss, ensuring the stability and performance of the fiber network.
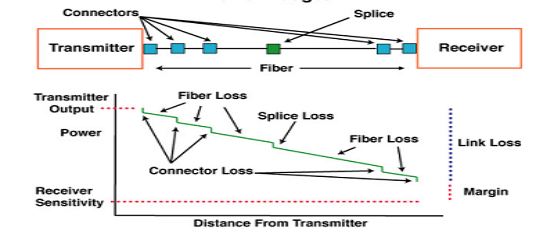
Polarity Errors
Polarity errors can prevent signals from correctly reaching the receiver, especially in parallel transmission scenarios with multiple fibers. To address polarity errors, use polarity test equipment during installation and maintenance to check the polarity of each patch cable, ensuring correct signal paths. Adhering to standardized cabling schemes and ensuring consistency in all connectors and patch cables can also effectively prevent polarity errors. Using professional polarity management software that can automatically detect and correct polarity errors further enhances polarity management efficiency. These measures ensure correct optical signal transmission, reducing network failures due to polarity errors.
Connector Wear and Aging
Over time, the mechanical performance of connectors degrades, reducing the number of insertion cycles and affecting connection quality. To address connector wear and aging, regularly replace frequently used connectors to ensure connection quality. Selecting durable MPO connectors designed for high insertion cycles can better resist wear and aging. Regular inspection and maintenance of connectors to promptly identify and replace faulty connectors can also effectively extend their service life. These methods ensure the long-term stable operation of the fiber network.

Installation Errors
Installation errors, including incorrect fiber patch cable connections, excessively long fiber links, or non-standard cabling, can affect the overall performance of the fiber network. To address installation errors, provide professional training for installation and maintenance personnel to ensure they understand the correct installation steps and standards. Establishing and following standardized installation procedures ensures each step meets the requirements. Using professional cabling tools and testing equipment to ensure installation quality is also crucial. These measures reduce the occurrence of installation errors, improving the performance and reliability of the fiber network.
Conclusion
MPO fiber patch cables play a vital role in modern data centers and high-density fiber networks, but they also face many challenges. By understanding and addressing these common issues, you can significantly improve the performance and reliability of MPO fiber patch cables. Whether it’s polarity management, connector cleaning, fault troubleshooting, or loss control, taking the right measures and using the right tools are key to ensuring the efficient operation of the fiber network.
If you’re looking for high-performance and reliable MPO fiber patch cables, FIBER-LIFE is your best choice. Our products play a crucial role in modern data centers and high-density fiber networks, not only enhancing network performance but also effectively solving common problems. We offer a variety of MTP/MPO cable assemblies, including MTP MPO trunk cables, MTP MPO branch LC cables, and cassette modules or patch panels, all strictly compliant with IEC standard 61754-7 and TIA 604-5.
At Fiber-LIFE, we also provide customization services, allowing you to adjust the number of fibers, cable type, and length according to your needs. By choosing our products, you’ll experience excellent performance in polarity management, connector cleaning, fault troubleshooting, and loss control, ensuring your fiber network operates efficiently. Visit our website now to purchase the MPO patch cables you need and take your network performance to the next level!