In the sophisticated domain of fiber optic communications, optical attenuators are indispensable for preserving the equilibrium and fidelity of signal transmissions. At FiberLife, we recognize the paramount importance of these minute components in ensuring that data transmitted across extensive networks arrives with clarity and precision. But what are optical attenuators, and why are they so vital to fiber optic systems? We are here to elucidate these critical elements, revealing their function, the variety of types available, and their significance for your fiber optic network.
I. The Essence of Optical Attenuators
An optical attenuator is an apparatus meticulously crafted to diminish the power level of an optical signal. In essence, it modulates the luminosity of light traversing the fiber optic cable. This may seem counter to expectations—why would one aim to attenuate the signal? The rationale is rooted in the necessity to uphold optimal signal potency. An excessively robust signal can overwhelm receivers, leading to distortion and data loss. By meticulously controlling signal strength, optical attenuators guarantee that the system operates within its ideal parameters.
Optical attenuators are primarily utilized in fiber optic communication systems to regulate the power level of signals. This regulation is essential as it averts the saturation of optical receivers, which can precipitate errors and a decline in communication quality. Attenuators find application in diverse scenarios, including the testing and calibration of equipment, balancing signal power in multi-channel systems, and adjusting power levels in long-haul fiber optic links.
II. The Fundamental Operating Principle of Optical Attenuators
Optical attenuators function by instilling a measured loss into the fiber optic link. They achieve this via several mechanisms:
- Absorption: The attenuator material absorbs a portion of the optical power, transmuting it into thermal energy. This process engages materials with specific absorption properties aligned with the wavelength of light traversing the fiber.
- Reflection: A fraction of the light is reflected back towards the source, curtailing the quantity of light that proceeds through the fiber. This technique often involves a slight discrepancy in the optical medium.
- Scattering: The light is dispersed in various directions, effectively reducing the potency of the transmitted signal. This can be accomplished through techniques such as employing a roughened surface or incorporating microscopic particles into the optical pathway.
These processes are finely calibrated to deliver a precise level of attenuation, enabling exact control over signal strength. Diverse types of attenuators harness these mechanisms in various combinations to attain the desired attenuation level.
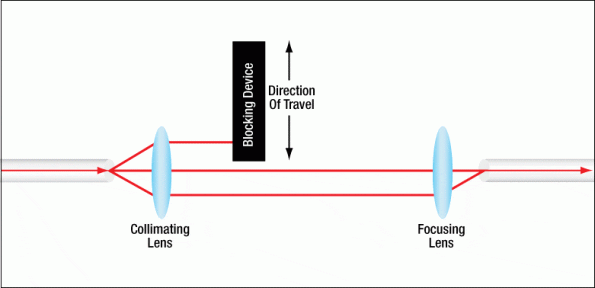
III. Varieties of Optical Attenuators
Optical attenuators manifest in a spectrum of forms, each tailored to distinct applications and requirements. Here is a comprehensive overview of the most prevalent types:
- Fixed Attenuators: These provide a constant level of attenuation that is not adjustable. They are typically employed in scenarios where the signal power necessitates a permanent reduction by a predetermined amount. These are straightforward and dependable for applications with unvarying demands.
- Variable Attenuators: These allow the attenuation level to be modified, offering the adaptability required for testing and maintenance tasks where signal levels may need frequent alteration. They can be manually adjusted or electronically governed, offering versatility in a range of scenarios.
- Step Attenuators: These offer discrete levels of attenuation, which can be altered in fixed increments. This design amalgamates elements of both fixed and variable attenuators, facilitating easy adjustments without the requirement for continuous tuning.
- In-Line Attenuators: Integrated directly into the fiber optic link, these attenuators are designed to be inserted into the fiber path, providing a constant level of attenuation. They are advantageous for long-term installations where spatial constraints and simplicity are paramount.
- Build-Out Attenuators: Also known as bulkhead attenuators, these are utilized at the connection points of fiber optic cables. They are ideal for applications where attenuation is requisite at the interface, offering a direct solution for managing signal strength at pivotal junctures.
IV. The Significance of Optical Attenuators in Fiber Optic Communication
- Signal Optimization: In fiber optic communication systems, maintaining the appropriate signal strength is indispensable. Optical attenuators are pivotal in ensuring that signals are neither excessively feeble nor overpowering. An overly weak signal can result in data loss and communication errors, while an excessively strong signal can induce distortion and overwhelm the receiver.
- Protection of Optical Components: Fiber optic components, particularly receivers, are sensitive to incoming signal power levels. Excessive signal strength can impair these components, leading to costly repairs and downtime. Optical attenuators safeguard these delicate components by regulating the power level, thereby enhancing the longevity and reliability of the entire communication system.
- Network Flexibility: Contemporary fiber optic networks are highly dynamic, with ever-shifting requirements. Optical attenuators supply the adaptability needed to accommodate these changes. Whether adjusting signal strength during network upgrades, managing diverse signal levels in complex installations, or testing new configurations, attenuators are essential tools that empower the network to meet a variety of evolving demands.
V. Conclusion
Optical attenuators are essential components in the sphere of fiber optic communication. They ensure that signals are conveyed at the optimal power level, safeguarding sensitive components and upholding the integrity of the communication system. With a multitude of attenuator types available, each suited to different needs, these devices provide the flexibility and reliability imperative in modern network infrastructures.
As our reliance on swift and efficient communication networks intensifies, the significance of optical attenuators will only escalate. Selecting high-quality attenuators from reputable manufacturers is vital for sustaining system performance. A compelling option to consider is the 0-30dB 1064nm Multimode Min MEMS Variable Optical Attenuator, which offers precise control over signal strength, ensuring peak performance and protection for your fiber optic systems.
Eager to augment your network with superior optical components? Visit our FiberLife website to discover more about our products and how we can assist you in achieving superior communication efficiency. Explore our comprehensive range of fiber optic solutions, and allow us to support you in maintaining a robust, adaptable, and high-performing network.