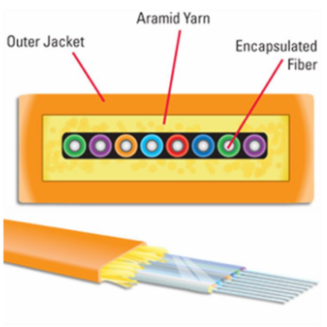
Ribbon fiber optic cables, crucial to modern fiber optic communication, are widely utilized in various network infrastructures due to their high density, performance, and reliability. As a leading supplier, FiberLife understands the importance of selecting the appropriate ribbon fiber optic cable to optimize network performance. We are committed to providing comprehensive solutions to assist you in navigating a complex and dynamic market. This blog offers an in-depth analysis of the various ribbon fiber optic cables available, highlighting their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and key selection factors to help you achieve efficient and reliable network construction. With our expert guidance, you will gain a better understanding of ribbon fiber optic cables and make informed purchasing decisions. FiberLife is here to help you build a stronger communication network!
Classification of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables
By Fiber Count
Ribbon fiber optic cables can be classified by fiber count into single-fiber and multi-fiber cables. Single-fiber cables are ideal for low-density communication needs, making them suitable for small-scale networks. In contrast, multi-fiber cables cater to high-density communication environments, enabling the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals, thereby enhancing data transmission efficiency. These are widely used in data centers and extensive network infrastructures.
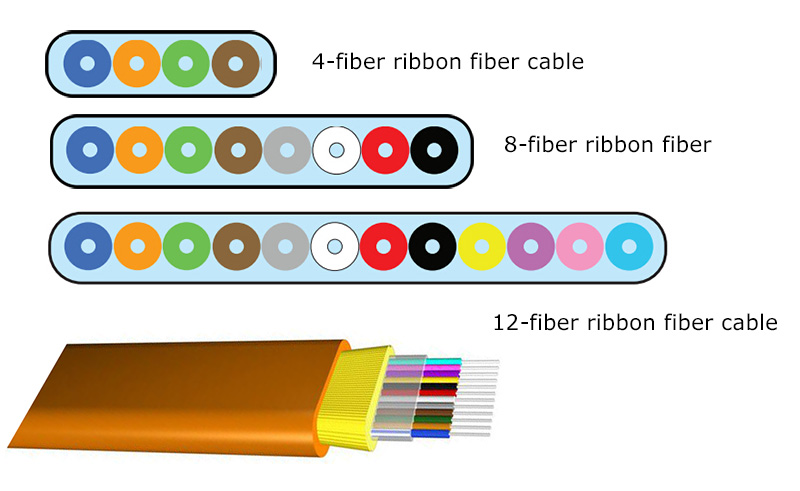
By Application Scenario
Based on application scenarios, ribbon fiber optic cables are divided into indoor and outdoor types. Indoor cables are designed to be lightweight and flexible, suitable for office buildings and data centers. They are easier to install in tight spaces. Outdoor cables, however, are built to withstand harsh conditions, featuring robust protective layers and waterproof designs to ensure reliable performance in varying environments.
By Structural Design
Structurally, ribbon fiber optic cables are categorized into tight-buffered and loose-tube types. Tight-buffered cables have a protective layer directly on the fiber, offering a compact structure with high tensile strength, suitable for high-stress environments. Loose-tube cables, with space around the fiber, provide installation flexibility, making them suitable for complex wiring environments despite their relatively lower tensile strength.
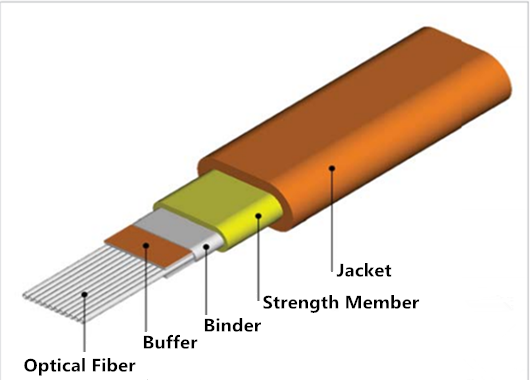
By Fiber Type
Ribbon fiber optic cables are also classified by fiber type into single-mode and multi-mode fibers. Single-mode fibers are suited for long-distance, high-bandwidth transmission with low signal loss, making them ideal for long-distance communication and core networks. Multi-mode fibers, used for medium to short-distance data transmission, are cost-effective and commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and within data centers.
Characteristics, Advantages, and Disadvantages
Single-Fiber vs. Multi-Fiber Cables
Single-Fiber: Simple structure, easy installation, high flexibility, and low maintenance costs. However, they have limited transmission capacity, making them unsuitable for high-density data centers.
Multi-Fiber: High transmission capacity, supporting large-scale data centers and backbone networks. They are more challenging to install and require specialized equipment, resulting in higher initial costs but offering significant long-term economic benefits.
Indoor vs. Outdoor Cables
Indoor: Lightweight, flexible, easy to install, and ideal for controlled environments. They lack environmental resistance, making them unsuitable for harsh outdoor conditions.
Outdoor: Robust, durable, and reliable under harsh conditions. They are heavier and more challenging to install, with higher initial and maintenance costs.
Tight-Buffered vs. Loose-Tube Cables
Tight-Buffered: Compact with high tensile strength, suitable for high mechanical stress environments. Installation flexibility is lower, requiring higher technical expertise.
Loose-Tube: Flexible installation, suitable for complex environments, and easier adjustment and maintenance. However, they have lower tensile strength and are more prone to deformation.
Single-Mode vs. Multi-Mode Fibers
Single-Mode: Long-distance, high-bandwidth transmission, suitable for backbone networks. They are costlier and require higher technical support.
Multi-Mode: Cost-effective for medium to short distances, suitable for enterprise LANs and data centers. They have higher signal loss and limited bandwidth, making them unsuitable for long-distance transmission.
Key Factors in Choosing Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables
Application Requirements
Identify specific application needs. Data centers require high-density multi-fiber cables, while long-distance transmission demands single-mode fibers.
Cost-Effectiveness
Balance initial installation costs with long-term maintenance. Single-mode and multi-fiber cables, despite higher initial costs, offer significant long-term benefits.
Future Scalability
Consider future network expansion needs. High-density multi-fiber cables provide more transmission channels, aiding future scalability.
Market Demand and Technological Impact
The ribbon fiber optic cable market is rapidly growing, driven by 5G deployment and data center expansion. Multi-fiber cables are in high demand due to their high-density transmission capabilities. Emerging technologies are enhancing the performance and adaptability of fiber optic cables, meeting diverse application needs.
Conclusion
Ribbon fiber optic cables are essential for modern communication networks, offering high density, performance, and reliability. FiberLife provides a wide range of ribbon fiber optic cables to meet various network needs, helping you build efficient and stable data transmission networks. Choose FiberLife for your network construction and experience the benefits of advanced fiber optic technology.
Act now and choose FiberLife’s ribbon fiber optic cables to build an efficient, reliable communication network. Let your data transmission soar with FiberLife, supporting every step to your success!