Multi-fiber push-on (MTP) cables are essential in fiber optic connectivity and are designed to facilitate and improve data transmission in high-performance networks. As technology advances, the demand for faster and more reliable communication systems continues to increase, so it is necessary for professionals to thoroughly understand MTP Cables.

01.Defining MTP Cables and Their Uses
Multiple optical fibers used in high-density fiber optic cables+ (MTP cables) are contained in a single connector+. Their main purpose is to enable efficient data transmission in large data centers and telecommunication networks. Server interconnects, network backbone connections, and structured cabling systems+ are just some of the applications they are designed for. Compared to traditional single-fiber cables, MTP cables allow for faster deployment and more straightforward scalability, which greatly reduces installation time and difficulty while providing better bandwidth support and more reliable links between devices.
02.Differences between MTP and MPO Cables
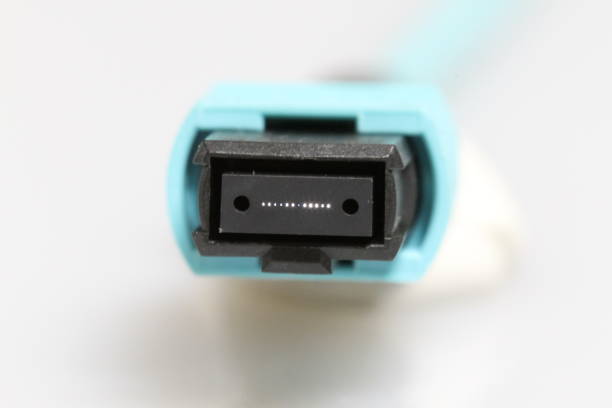
MTP (Multi-Fiber Terminated Push-On) and MPO (Multi-Fiber Push-On) cables are often considered the same due to their similar appearance, but there are actually some differences between them. Invented by USConec, MTP cables are designed to achieve better performance and reliability: they have a patented design that allows for more alignment options and higher-density configurations. In terms of connector design, MTP connectors have additional features compared to regular MPO connectors, such as reduced insertion loss and a stronger locking mechanism, while regular MPO connectors may not have very good alignment effects.
In addition, MTP cables are available in different configurations, including custom lengths and fiber counts, allowing flexibility to meet specific network requirements. To summarize the above points, both MTP and MPO cable types play an important role in fiber optic networks. However, MTP lines are more suitable for high-performance applications because these products have advanced features that are derived from the superior engineering processes used in their manufacturing process.

03.Key Components of MTP Fiber Optic Cables
MTP fiber optic cables contain several important components that help improve the performance of telecommunications networks.
Optical Fibers: These are the main components of MTP cables and transmit data in the form of optical signals. They can be single-mode or multimode; single-mode is used for long-distance communication, while multimode has a larger core diameter and therefore works best over short distances.
Connector Housing: The MTP connector housing is made of solid materials, which is durable and resistant to environmental pressures. Its structural design makes it easy to assemble and disassemble, making maintenance simpler.
Alignment Mechanism: To ensure the connectors are properly aligned, MTP connectors use high-tech alignment systems (like guide pins). This is extremely important as it reduces insertion loss and improves overall signal quality.
Protective Sleeve: Environmental factors like moisture and dust can damage the optical fibers, so a protective sleeve is included in MTP cables to prevent this from happening. However, to maintain the integrity of these fibers over the long term, they also need to be protected from any other physical damage.
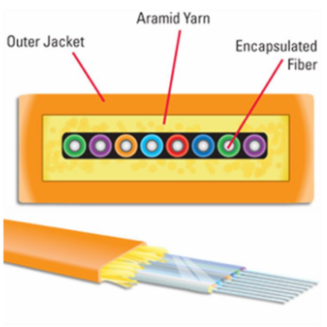
Cable Jacket: The outer jacket of the cable, made from rugged materials like PVC or LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen), provides additional shielding for the components inside. These materials do not produce toxic emissions when burned, thus improving fire safety.
Strength Members: During installation/operation, Aramid Yarn+ or Fiberglass Rods provide support in strength members integrated into the structure of the cable reinforcement system, meaning that pulling forces will not have an impact on performance levels. The best is the strongest.
The synergy between these elements enhances the functionality of MTP fiber cables, making them ideal for high-density network environments that require best-in-class performance and reliability.
04.How to choose the right MTP connector?
Types of MTP connectors: APC, MPO, etc.
To choose an MTP connector, it is important to distinguish between different types for specific uses
APC (Angled Physical Contact): These 8-degree angle connectors have minimal back reflections and are ideal for tasks that require high precision and low signal loss.
MPO (Multi-Fiber Push-On): These connectors allow multiple fibers to be terminated in one connector, thereby increasing cable density while minimizing installation time. They are widely used in data centers and telecommunications.
MTP (Multi-Fiber Termination Push-On): This is an improved version of MPO with better alignment.
Standard vs. Custom Configurations: There are standard MTP connectors, but custom configurations can be developed with specified fiber count and length options to meet specific network needs.
Selecting the appropriate type of MTP connector ensures optimal performance and compatibility within the network system.
Considerations for High-Density Environments
To optimize performance and maintain reliability when working in high-density environments, there are several important factors to consider.
Space Constraints: Limited physical space is often an issue for high-density layouts. Using MTP connectors that support the optimal number of fibers in a compact configuration is critical to maximizing the available area.
Heat Dissipation: Increased cable density leads to higher temperatures, which can affect performance. Proper airflow and cooling mechanisms should be ensured to prevent overheating. Heat.
Cable Management: Effective cable management solutions are needed to prevent cable tangles and keep pathways organized. Trays, brackets, and labels allow for easy access and maintenance.
Future Scalability: To adapt infrastructure to changing needs over time, it is imperative to ensure that modular and flexible MTP solutions are selected to allow for potential expansion of fiber count or network capabilities.
Network administrators addressing these considerations will help improve the efficiency and longevity of fiber systems in high-density scenarios.
05.MTP Connectors for Different Fiber Applications
MTP connectors are adaptable solutions used in a variety of fiber applications to ensure optimal performance and connectivity.
Data Centers: MTP connectors are used in data centers due to their high-density deployment capabilities and fast data transfer rates. Due to their modularity, they can be easily configured to work in dynamic networks.
Telecommunications: In this industry, MTP functionality is a critical backbone infrastructure. These types of connections are considered reliable and versatile to support a variety of communication applications while efficiently managing large volumes of traffic.
Local Area Network (LAN): Today, there has been an increase in the use of MTP connector configurations in LANs as a way to provide high-speed connections between network switches and server racks. The design allows multiple fibers to be placed into a smaller space, maximizing bandwidth where it is needed most.
06.MTP Cable vs. Traditional Fiber Optic Cable
MTP cables have some key differences compared to traditional fiber optic cables that highlight The advantages of MTP technology are shown in Figure 1. First, MTF cables are multi-fiber connectors +, allowing multiple fibers to be terminated within a single connector. This provides a high-density solution for environments with a large number of cables but limited space. On the other hand, traditional fiber optics typically use a single connector, which results in a larger and more complex installation and management process.
Second, MTP components are designed for rapid deployment compared to traditional fiber optic systems, so installation time can be significantly reduced. This efficiency not only reduces labor costs, but also reduces the possibility of errors during installation. In addition, MTP connectors are able to maintain excellent signal integrity while reducing insertion loss, thereby ensuring better reliability and performance, which is critical for applications that require high bandwidth. In summary, while standard optical fibers provide reliability, they cannot meet the needs of modern networks like MTP because they are more efficient, space-saving, and more scalable.

07.How to Install and Maintain MTP Cables?
MTP Cable Installation Step-by-Step Guide
Preparation: Prepare all tools and materials required for installation, such as MTP cables, connectors, cleaning supplies, and termination tools.
Planning Layout: Determine the installation route by considering cable length, bends, and possible obstructions to ensure an efficient and organized setup.
Cable Routing: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines when terminating MTP connectors, while ensuring that each fiber is properly seated within the connector housing before tightening.
Connector Termination: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines when terminating MTP connectors, while ensuring that each fiber is properly seated within the connector housing before tightening.
Test Connections: Optically test each connection using a suitable light source and power meter to verify its integrity and performance level
Label: Clearly label all cables and connectors to facilitate future maintenance work or troubleshooting processes
Documentation: Installation details, including the cable path taken to reach the termination point where the test results were obtained, should be recorded to create accurate system documentation for later reference.
Regular Maintenance: Schedule regular inspections and performance tests+ to check that the system continues to be reliable.
08.Common Maintenance Techniques for MTP Fiber I5
Routine Inspection: Visual inspection of MTP cables and connectors should be performed regularly to detect any signs of wear, damage or contamination that may affect performance.
Cleaning Methods: Use appropriate cleaning methods and materials manufactured specifically for fiber optic connectors to remove dust and debris that may cause signal loss. All connectors must be cleaned before each use.
Monitoring Performance: Continuous performance monitoring should be performed using optical test equipment to detect any anomalies in signal quality, allowing timely intervention when necessary.
Environmental Considerations: Optimal environmental conditions must be maintained to avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity or physical stress, as these may cause damage to its integrity.
Proper Storage: When not in use, MTP cables should be kept in protective boxes/racks to prevent them from physical damage/kinking, thereby extending their service life.
Document Updates: Maintenance logs should always be kept up to date, recording all inspections completed, tests conducted and actions performed, leading to a more informed approach to system management.
09.Understanding MTP Cable Standards and Specifications
MTP Cable Types: OM3, OM4, and Others
- OM3 Cable: OM3 multimode fiber + is designed for 10GbE applications, with a maximum modal bandwidth of 2000MHz:km. The former supports distances up to 300 meters, and the latter supports distances up to 400 meters.
- OM4 Cable: Unlike OM3, OM4 cable further enhances its performance to support 10GbE distances of 400 meters and 40GbE/100GbE up to 150 meters, with a modal bandwidth of 4700MHz·km.
- OM5 Cable: OM5 is the latest multimode fiber standard that enables short wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM) applications. Its modal bandwidth is 5000MHz·km, and the transmission distance can reach 200 meters at a rate of 100Gbit/s.
These MTP cable types are very important for optimizing network performance and should be selected based on the specific requirements of each fiber installation type.
010.Frequently Asked Questions About MTP Cables
MTP vs. MPO: What’s the Difference?
The types of multi-fiber connectors used in high-density fiber installations are MTP (Multi-Fiber Termination Push-On) and MPO (Multi-Fiber Push-On). The two connectors differ in their design and performance capabilities. In fact, MTP connectors belong to the broader MPO connector group but offer superior optical performance through better alignment accuracy, higher data rate support, and lower insertion loss, among other things. Additionally, removable housings and enhanced durability make MTP connectors ideal for use in more challenging conditions. Conversely, while all MTPs are considered MPOS compliant, not every MPO meets the mTp specification.
How to Test and Verify MTP Connections
MTP connections should be tested for integrity and performance using an optical power meter and a light source or an optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR). First, clean all connector ends to prevent contaminants from affecting the measurement. Next, connect a light source to one end of the MTP cable and an optical power meter to the other end. Measure the optical power level within the acceptable range and according to the system specifications. For more analysis, use an OTDR to identify potential faults along the fiber path that could degrade its performance, such as breaks or bends. Recording each test result to demonstrate compliance with industry standards also helps with troubleshooting when problems arise.
MTP Fiber Cable and Transceiver Compatibility
For high-density data center applications, MTP fiber cables can be used with multiple types of transceivers. Most modern transceivers are available in 10G, 40G, 100G, and even 400G standards, which can connect well with MTP connectors. Commonly used compatible transceiver modules are SFP+ for 10G connections and QSFP+ or QSFP28 for 40G and 100G connections. These modules use MTP connectors to create branch configurations or aggregate connections that can accommodate multiple fibers in one connector. It is important to ensure that the optical specifications of the transceiver match those of the MTP cable used, especially single-mode vs. multimode compatibility, as well as the appropriate wavelength for the specific application. Regularly checking compatibility not only ensures optimal performance, but also improves network reliability.