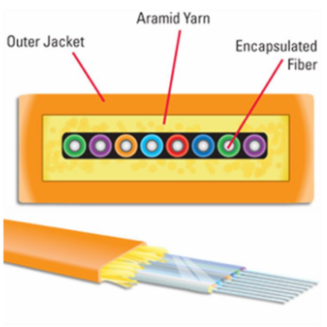
Optical fiber is a light-conducting fiber made of glass or plastic that uses the principle of total internal reflection to transmit light in these fibers.

What are the characteristics of optical fiber?
- If the optical fiber is encapsulated in a plastic protective cover, it can bend and will not break, making it an excellent signal transmission tool.
- The loss of optical fiber during transmission is much lower than the loss of electricity in wires. The current better optical fiber has a light transmission loss of only 0.2 decibels per kilometer; that is, only 4.5% is lost after one kilometer of transmission; so now long-distance electricity transmission uses high-voltage lines to reduce the loss of electricity.
- The main raw material of optical fiber is silicon, which has a huge reserve, is easier to mine, and is relatively cheap; the content in our earth’s crust is only lower than the oxygen content, accounting for about a quarter of the surface rock, but there is a disadvantage that silicon is mainly in the form of oxygen-containing compounds, so in industry, it is necessary to use high-purity C (carbon) in an electric furnace for reduction reaction.
What is the principle of optical fiber?
Optical fiber is a cylindrical dielectric waveguide that uses the principle of total internal reflection to transmit light. Since there is no light loss during reflection, the signal can be transmitted to a very long distance.
So what is the principle of total internal reflection?
In layman’s terms, this is an optical phenomenon. When light passes through two media with different refractive indices, part of the light will be refracted at the interface of the media, and the rest will be reflected. However, when the angle of incidence is larger than the critical angle (the light is far away from the normal), the light will stop entering the other interface and all will be reflected inward!
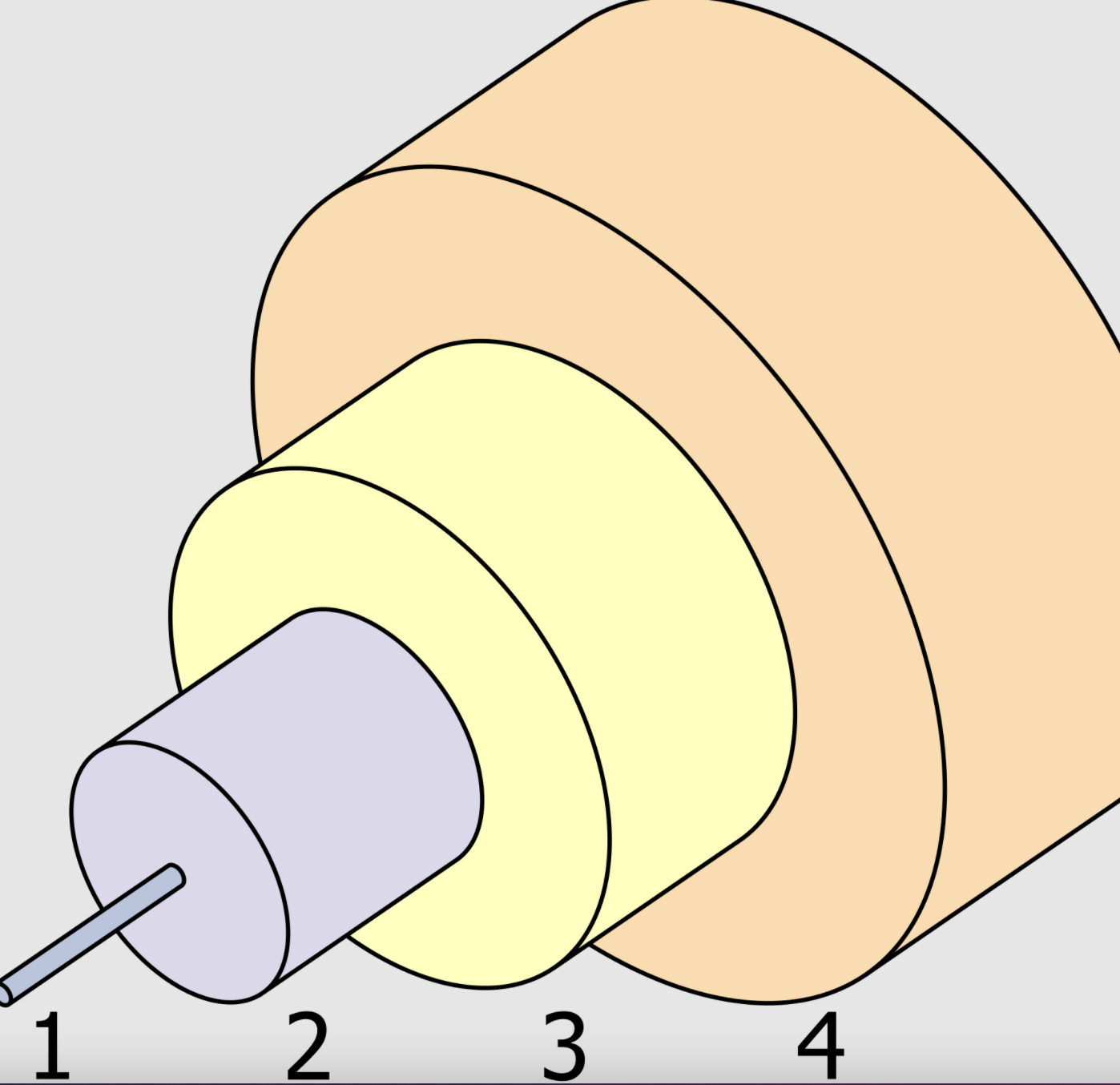
Internal structure of single-mode fiber optics: 1. Core: 8 µm in diameter 2. Cladding: 125 µm in diameter 3. Buffer layer: 250 µm in diameter 4. Jacket: 400 µm in diameter
- Currently, the optical fiber used in communications is mainly glass fiber, with an outer diameter of about 250 microns and a central light-transmitting part with a diameter of 10 to 60 microns.
- The structure of the optical fiber is roughly divided into the inner core part and the outer cladding part.
- In order to confine the optical signal to the core, the refractive index of the cladding must be less than the refractive index of the core. The refractive index of the graded-index optical fiber changes slowly, gradually decreasing from the axis to the cladding; while the refractive index of the abrupt-index optical fiber changes sharply in the core-cladding boundary area.
Can you imagine a world without fiber optics?
- What you can see now is not so common, e-sports games, short video applications, 5G networks, driverless cars, instant messaging, live shopping and other things related to the Internet
- How to understand it, all instant messaging may be based on satellites, which is fine for international communications, but the price is extremely unfriendly to ordinary people
- It will not happen that you read my article with your mobile phone while I write this article leisurely
Finally, I have to mention here a great electrical engineer: Mr. Kao. It is because of his contribution that we can enjoy today’s Internet world. He solved how to build a high-speed Internet highway in the virtual world so that people all over the world can truly be in the same world