Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) is a pioneering optical technology that revolutionizes bandwidth capabilities across existing fiber optic networks. In the realm of traditional optical fiber networks, a single lightbeam dances alone through the fiber, carrying information. But in the symphony of Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) networks, the fiber’s vast optical bandwidth is divided into multiple wavelength channels, each conducting its own distinct data stream. When this multitude exceeds 20 channels, the system earns the title of Dense WDM, or DWDM.
What Is DWDM?
DWDM, a marvel of modern optics, is employed to amplify the bandwidth of existing fiber optic networks. It operates by harmoniously combining and transmitting multiple signals on different wavelengths along the same fiber strand. This technique transforms a single fiber into a multitude of virtual fibers, thereby multiplying its capacity. For instance, by integrating eight OC-48 signals into one fiber, the carrying capacity escalates from a mere 2.5 Gb/s to an impressive 20 Gb/s. DWDM can transport up to 80 wavelengths within the C band spectrum, all nestled in the 1550nm region, a testament to its protocol- and bit-rate independence, making it versatile for IP, ATM, SONET/SDH, and Ethernet transmissions.
Advantages of DWDM
DWDM is the architect of long-haul transmission, where wavelengths are compactly packed, offering a high-capacity solution in telecom networks. It enables an increased number of channels within the same fiber, with dispersion compensation applied effortlessly. DWDM resides entirely within the C-band, where attenuation and dispersion are significantly lower than in other bands. Furthermore, DWDM leverages the operational window of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) to amplify optical channels, extending the system’s reach to over 1500 kilometers. The adoption of DWDM technology stands as the pinnacle of cost-effective transport, merged with advanced functionality, designed to manage the surging bandwidth demands from access networks.
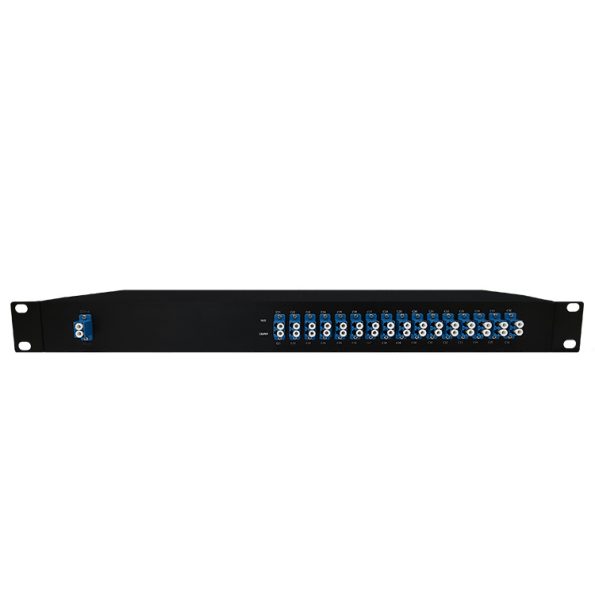
DWDM Equipment
DWDM is the cornerstone of optical transport networks. Its essential components form a well-orchestrated system. The transmitter, or transmit transponder, kicks off the process by converting electrical bits into optical pulses with laser precision. The multiplexer and demultiplexer then weave their magic, respectively merging and separating these discrete wavelengths. The link, a strand of optical fiber with minimal loss and stellar transmission performance, is complemented by flat-gain optical amplifiers that boost signals across longer spans. Finally, the receiver, or receive transponder, translates optical pulses back into electrical bits, ensuring the message’s clear delivery.
FiberLife: Your DWDM Solutions Provider
FiberLife offers an expansive array of DWDM products, designed to construct and expand fiber optic networks with ease. Our offerings include DWDM MUX DEMUX modules with 50GHz/100GHz/200GHz channel spacing, DWDM OADM modules in various configurations, and DWDM transceivers capable of supporting data transmissions from 155Mbps to 10Gbps.
Conclusion:
DWDM stands as a testament to optical innovation, a technology that not only meets but exceeds the demands of today’s bandwidth-intensive world. As we look to the future, DWDM continues to pave the way for more efficient and powerful data transmissions across the globe.