Now, the demand for backbone optical cables in enterprise networks has far exceeded the supply, and balancing this demand relationship has become a top priority. The simplest way to solve this problem is to lay more backbone optical cables, but this is also the most expensive solution. Therefore, in order to save costs, technologies such as time division multiplexing (TDM) and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) have emerged. The principle of these technologies is to multiplex multiple signals onto one optical fiber for transmission, thereby saving optical fiber resources. Among them, DWDM technology is currently a very popular wavelength division multiplexing technology. This tutorial will explore how to upgrade the network to 500G using a 40-channel DWDM multiplexer/demultiplexer.
DWDM multiplexer/demultiplexer – a solution that saves the most fiber resources
DWDM is a laser technology used to increase bandwidth on existing fiber backbone networks. More precisely, the technology multiplexes the tight spectral spacing of a single fiber carrier in a specified fiber to achieve the purpose of transmitting multiple signals with one fiber. In this way, the total number of fibers required can be reduced under a given information transmission capacity. DWDM multiplexers/demultiplexers can provide large-capacity, diversified broadband services, allowing network operators to increase the transmission bandwidth to 16, 32, 64 or even 128 times at an effective cost. Current DWDM multiplexers/demultiplexers can provide a single-fiber transmission capacity of 16/20 or 32/40 waves, up to 160 waves, with flexible expansion capabilities.
How does a DWDM multiplexer/demultiplexer increase bandwidth?
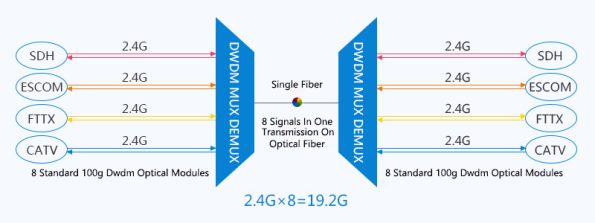
DWDM multiplexers/demultiplexers can combine and transmit different wavelengths simultaneously in the same fiber. For example, it can multiplex 8 fiber carriers, that is, transmit 8 signals in one fiber, so that the transmission capacity will be increased from 2.4Gb/s to 19.2Gb/s (now the transmission capacity of a single wavelength on a single fiber is usually 2.4Gb/s). A key advantage of DWDM multiplexer/demultiplexer is that its protocol and transmission speed are irrelevant. DWDM-based networks can use IP protocol, ATM, SONET/SDH, Ethernet protocol to transmit data, and the data traffic processed is between 100Mb/s and 2.5Gb/s.
Upgrading to 500G with a 40-channel DWDM mux/demux
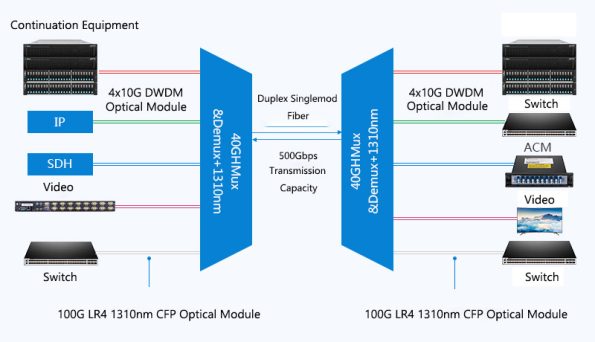
Nowadays, the optical modules used with DWDM mux/demux are usually DWDM SFP+ optical modules, so the transmission rate of each wavelength is 10Gbps. In this way, if we use a 40-channel DWDM mux/demux, we can achieve a transmission rate of 400Gbps through a pair of optical fibers. So how to achieve 500Gbps with a 40-channel DWDM mux/demux? This requires the use of the 1310nm port on the 40-channel DWDM mux/demux, which is an additional broadband optical port. When all ports on the 40-channel DWDM mux/demux are occupied, optical devices can be connected through the 1310 nm port.
It should be noted that the working wavelength of the optical module connected to the 1310 nm port must be 1310 nm, such as 40G LR4 1310nm QSFP optical module, 40G ER4 1310nm QSFP optical module and 100G LR4 1310nm CFP2 optical module. Now let’s go back to the question mentioned in the previous paragraph: How to achieve a transmission rate of 500Gbps with a 40-channel DWDM multiplexer/demultiplexer? As mentioned above, a 40-channel DWDM multiplexer/demultiplexer can achieve a transmission rate of 400Gbps through a pair of optical fibers, and the remaining 100Gbps can be achieved through the 1310 nm port. You only need to use a fiber jumper to connect the 1310 nm port to the 100G LR4 1310nm CFP2 optical module on the terminal device (Ethernet switch, router, etc.), and the entire DWDM system can achieve a transmission rate of 500Gbps. The specific example is shown in the figure below: